How to grow gardeners' favorite - remontant raspberry Polka in the country
Content
The history of growing raspberries Polka
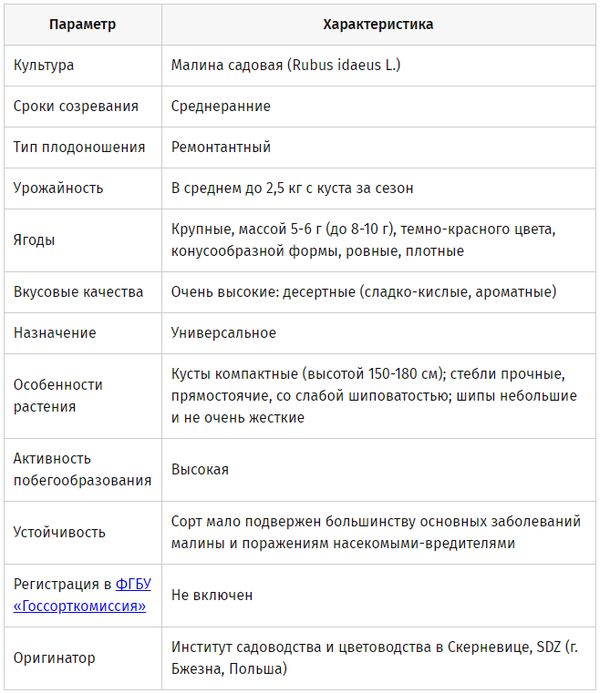
The repaired variety was bred by the Pole Jan Danek in 1993. A breeder from the Brzezno Institute of Horticulture and Floriculture crossed Autumn Bliss with the P89141 group. Despite the good reviews, the raspberry Polka (or Polka) was first presented at the Berlin Fruit Focus exhibition only 10 years later. After international recognition, it began to grow in many European countries and is now ranked first in industrial cultivation.

Video "Caring for raspberries after fruiting"
In this video, an expert will tell you how to care for raspberries after fruiting.
Description and characteristics of the variety
Gardeners love the Shelf very much for its high yield and long-term fruiting. Another advantage of the remontant variety is ease of maintenance. In addition, raspberries are resistant to many diseases. Below we will provide a brief description of the hybrid.
Botanical portrait of bush and berries
The shelf is a medium-sized shrub up to 1.8 m high. Possessing a powerful rhizome, one seedling gives up to 10 strong upright shoots. The branches are covered with small soft thorns. Raspberry fruits are large (2-3 cm), ruby-red, pyramidal elongated shape. The variety is distinguished by a small bone, as well as a dessert taste with sourness. One fruit branch can hold up to 6 berries, 5-10 g each.
Features of fruiting and productivity
Raspberries begin to bear fruit in mid-summer, and the berries ripen even on annual seedlings. Two-year-olds are covered with ripe fruits a little later - by the end of August. In this case, the crop can be harvested for 3 months, until the first frost. Subject to all agrotechnical rules of cultivation, one bush gives up to 2.5 kg of juicy berries.
Commercial and consumer qualities of berries
The fruits of the Shelves have a dense structure, and therefore well tolerate long-term transportation. At a temperature of + 3 ... + 6 ° C, they can be stored for several days without losing marketability. Outwardly, the berries look very attractive, they have a pronounced raspberry aroma. Thanks to their fleshy pulp, they can be frozen or processed in any way.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
The Repair Shelf, like many other varieties, has its own advantages and disadvantages.
- balanced taste;
- external aesthetics;
- possibility of transportation over long distances;
- resistance to fungal diseases;
- weak degree of studding;
- high productivity.
- weak frost resistance;
- instability of the root system to bacterial infections;
- sensitivity to extreme heat, lack of moisture.
Landing features
To make raspberries feel comfortable, it is enough to create the necessary conditions for them at the very beginning of growth.
Landing dates
Gardeners recommend planting seedlings in the fall. Before the first frost must be at least 21 days, otherwise the "young" will not have time to acclimatize. Planting can be carried out in the spring, but this must be done before bud break.
Raspberries with a closed root system can be transplanted at any time of the year, from early spring until the soil freezes.
Choosing a place, soil and planting material
The shelf loves light very much, so it is better to plant it on the south side of the site, protecting it from being blown by the wind. Highlands and lowlands with stagnant moisture should be avoided.
Raspberries prefer slightly acidic, loose, nutritious soil. If loams predominate in the garden, they can be diluted with sand, and for fertility, increase the amount of fertilizing.
Do not take too large planting material, otherwise it will take root for a long time in a new place. The root system should be well branched, without noticeable damage.

Secrets of planting seedlings
The soil for the "young" begins to be prepared 14 days before planting. For a seedling to take root well and develop quickly, it is enough to follow a simple algorithm:
- Dig out 50x40 cm landing holes at 1 m intervals.
- Pour the nutrient mixture (superphosphate, potassium sulfate, manure) to the bottom.
- Place the seedling, carefully spreading the roots.
- Cover with soil, leaving the replacement bud 5 cm above ground level.
- Sprinkle 10 liters of water abundantly.
- Lay out a mulch layer of dry grass or peat.
Caring for the remontant variety Polka
Caring for the Shelf is no different from other raspberry varieties. The main thing is to carry out all the necessary procedures in a timely manner.
Watering and loosening
The moisture-loving shrub does not like dry soil, and therefore needs regular watering. Each plant takes up to 30 liters of water.
In order for raspberries to receive all the nutrients in the right amount, the soil under it is periodically loosened. The first time the procedure is carried out in early spring, then it is repeated 6 times throughout the season.
Balanced diet
The shelf is very fond of a highly nutritious environment, so feeding is carried out repeatedly:
- in early spring - organic fertilizers;
- in the summer, every month - potassium-phosphorus compositions;
- in the fall - organic.
Garter and bush formation
Despite strong shoots, raspberries need to be tied up. This will prevent them from breaking, keep the berries from falling into the ground, and make picking more convenient. According to gardeners, it is better to fasten the Shelf to the wire mesh in a fan-like manner.
If the culture is grown as an annual, then after the first fruiting, pruning is carried out at the root. In order for the plant to produce a crop twice per season, it is pruned in a different way. Before wintering, the top of the shoots is cut off without affecting the viable bud.
- Raspberry garter
- Tying stalks to stakes
- Raspberry pruning
Preparing for winter
The shrub can be prepared for winter in different ways:
- with a complete cut of the shoots, the plant is mulched with a thick layer of dry grass, sawdust or peat;
- leaving the raspberries for the second year, they are tied, carefully laid on the ground and covered with spunbond.
Reproduction of culture
Among gardeners, there are two main methods of breeding Shelves:
- separation from the bush;
- grafting.
In the first case, the root system is divided into parts, and then planted in a new place. Planting is best done in cloudy weather with light rainfall.
The second method is growing from a cut shoot.The lower part is slightly cut with a knife and placed in the Kornevin solution. As soon as small roots appear, the shoot is planted under the jar, creating greenhouse conditions for it.
A young plant is moved to a permanent place in the second year.
Prevention of diseases and pests
Raspberry Polka is not particularly susceptible to fungal infections, but the following diseases can affect it:
- root cancer - it is treated by cutting off the affected parts and treating them with copper sulfate;
- verticillary wilting - spraying with "Fundazol" or "Vitaros" will help;
- root rot - you can get rid of the disease with the help of fungicides.

If the affected area is extensive, the bush is dug up and burned.
Pest insects rarely grow on the plant. This can be aphid, raspberry moth, or may beetle. Fight them with insecticides or lime solution.
Dessert raspberry Polka is very loved by many summer residents. It gives a large harvest, and its berries have a lot of useful properties. Undemanding care and planting allows even beginners in gardening to grow this variety.



