Strawberry seedlings according to the Frigo method: characteristics and technology
Modern gardening technologies greatly facilitate the process of planting plantations, growing strawberries and allow you to get a large harvest all year round. Everyone knows that the fruiting of the bushes directly depends on the quality of the planting material. For this, the so-called Frigo strawberry seedlings are used, which are stored for a long time in a frozen state with an open root system.
Content
What is the effectiveness of the Frigo method?
In late autumn, with the help of special equipment, seedlings of Frigo strawberries are dug out. After that, it is cleaned, excess vegetation is removed, sorted into classes and packed for storage. The processing of seedlings is carried out in an equipped room with a constant air temperature of 12-14C, within 48 hours. Then the processed bundles are placed in a storage chamber, where high humidity 85-90% and low temperature 0-1C are observed. Strawberries can be stored in this frozen form from several weeks to 9-10 months. Plants begin to bear fruit within 7-9 weeks after planting.
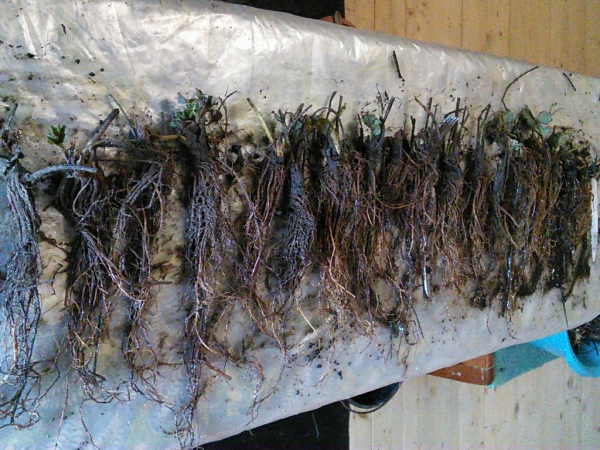

The peculiarity of this method is that the bushes do not overwinter on the ridges, where they can be exposed to various unfavorable factors. Thus, you can get a high yield of quality berries at any time. If you organize the correct planting of seedlings at different times, you can get a continuous fruiting cycle, which is very important for large farms and entrepreneurs.
In addition, this technology allows without damage to plants, it is convenient to transport planting material at any distance. A well-developed root system at the planting site ensures quick adaptation and survival. In this case, all the nutrients accumulated by the plant are used for the harvest, and not for the development of the bush itself.
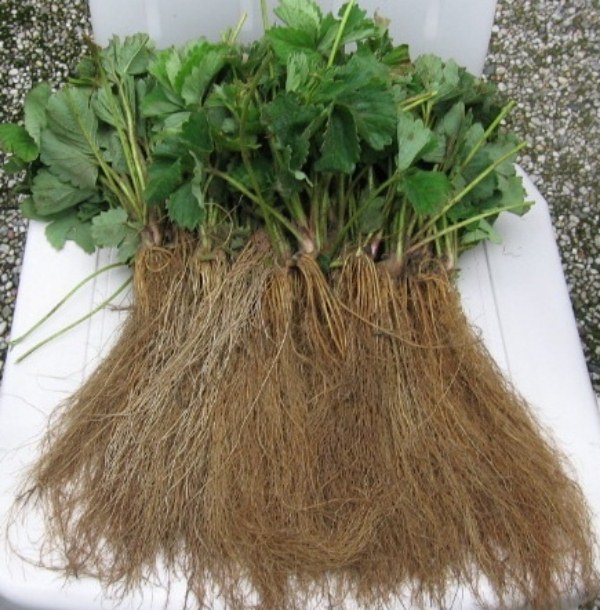

Cons of "frigo" seedlings
The most significant disadvantage of Frigo strawberry seedlings is the need for expensive special equipment for its processing and further storage, and, as a result, the high market value of this product. In order for the roots to give a good harvest, to be stored for a long time, the temperature in the storage must be constant. The slightest fluctuation even in 0.2-0.6 C can lead to freezing of the roots or premature germination of flower buds. In addition, a specialized device is also needed to maintain a stable high humidity, at least 85-90%.
It is rather difficult and energy intensive to grow such seedlings on the territory of Ukraine, Russia, Belarus. This is explained by unfavorable weather conditions and a relatively short growing season.
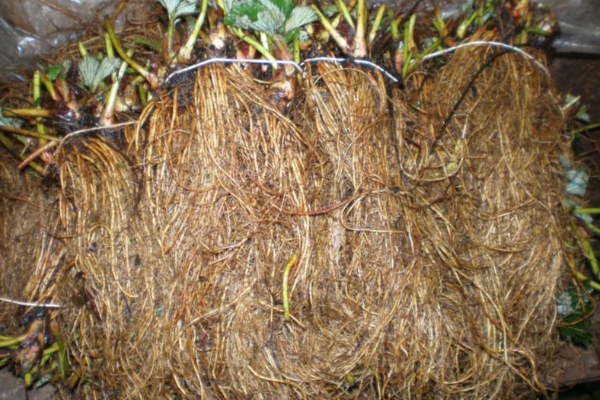

Varieties and classes
According to the established European standards, Frigo strawberry seedlings are divided into 4 main classes according to the diameter of the neck of the shortened shoot - part of the seedling from the rosette of leaves to the roots.
Plants of class B - neck diameter is 8-12 mm. They form only one peduncle and are often used for harvesting in subsequent years after planting. Why the peduncle is regularly removed.
Class A plants - neck diameter 12-15 mm. Fruiting begins in the current year of planting with proper transplantation and care. They give at least 2-3 peduncles and a guaranteed minimum productivity of 150-250 g.
Plants of class A + - neck diameter 15-18 mm.They can be stored for a longer period in comparison with the previous classes, therefore they are especially valuable for planting large-scale plantations with a late harvest. Although their cost is much higher, they bear fruit well in the first year after planting - 9-11 t / ha, covering all costs.
Plants of class A + extra - neck diameter 20-24 mm. They usually have lateral horns and form 4-6 fruits, which increases their yield to 450-500 g of berries from one bush, depending on the variety. The survival rate is fast and 100%. However, the cost of seedlings of this class is the highest.

It should be noted that regardless of the type of seedlings, Frigo is several times superior to ordinary strawberries in all its characteristics and significantly exceeds its yield.
Planting and leaving
If a one-time use of the plantation is planned, then the plants are planted compacted with a distance between the rows of at least 18-25 cm in order to avoid excessive thickening and crushing of the berries. With a two-year cycle, an ordinary or two-line planting is used with a distance between rows of 85-95 cm, between lines - 45-55 cm, between bushes 25-35 cm.
Thawed seedlings should be immediately planted in well-moistened, enriched soil, without leaving it with exposed roots for more than 10-15 minutes. To maintain the distance between the bushes, special markers are used. Since the seedlings do not have leaves, they are especially careful when planting that the heart is slightly above the soil level. The roots are placed in a hole, straightened in different directions, sprinkled with earth, compacted with your hands and mulched with straw, sawdust or needles. Water abundantly. The first 8-10 days after planting, you should maintain high soil moisture by watering the plants every day, then watering is carried out once every 5-6 days, and during flowering and before the first ovaries appear, watering is reduced to once every 7-9 days.
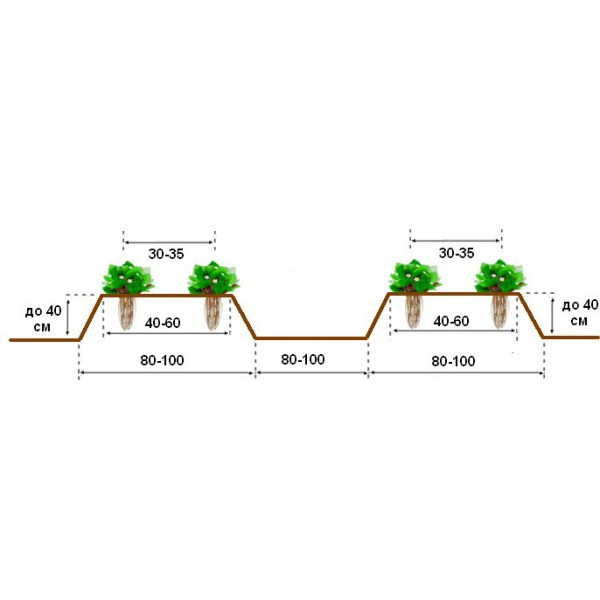
Planting scheme for Frigo strawberry seedlings
During the ripening period of small ovaries, 2-3 fertilizing with nitrogen-containing fertilizers is carried out, 15 g per 6-8 liters of water. At the same time, make sure that the solution does not get on the leaves or berries, since it can provoke the appearance of rot on them. Throughout the growing season, it is necessary to monitor the cleanliness of the planting, removing all weeds in time. During the ripening period of berries, the plantation is watered after each harvest. At the end of fruiting, with a single planting, the plants are completely removed. If the plantation remains for another year, the mulching layer is removed and the bushes are fed with complex fertilizers and potassium sulfate, while nitrogen-containing fertilizers are not advisable to apply. Then the strawberries are covered for the winter with perforated film, lutrasil or agrofibre.
Video "Technology of growing strawberries in low-volume hydroponics"
This video shows the sequence in which hydroponic cultivation is carried out.
