Fertilizer for early plants superphosphate: composition and method of application
Content
Fertilizer composition
The main component of superphosphate is phosphorus. Its content varies from 26 to 50%, depending on the type of fertilizer. The second component of superphosphate is nitrogen, its concentration is 6-17%. The fertilizer also contains some trace elements usually found in phosphorites: magnesium, calcium, potassium, sulfur. Fertilizer is a complex mixture that has two main types:
- Superphosphate is simple. It is obtained in the process of processing phosphorites with sulfuric acid. It is a powder containing up to 26% phosphorus, 6-8% nitrogen, 10% sulfur and 40% calcium sulfate (insoluble gypsum). Gypsum does not bring any benefits to crops, but due to its presence, the top dressing does not cake. From simple powder superphosphate, granular is produced - loose fertilizer in the form of granules with a diameter of up to 4 mm. It dissipates better and is considered more beneficial for plants, as it contains less gypsum (30%).

- Double superphosphate. To obtain it, phosphorite is treated with phosphoric acid, due to which the dressing contains more phosphorus (up to 50%) in an easily digestible form and practically does not contain gypsum. The fertilizer also contains more nitrogen (17%) and 6% sulfur. Double superphosphate is produced only in granular form.
On sale you can find several types of fertilizers with additional components: ammonized superphosphate (contains 1.6% ammonia, used to neutralize soil acidity), and superphosphate with humates (humic acid salts, used to increase soil fertility).
Video "Preparing plants for winter"
How to prepare plants for the winter period with the help of dressings.
What is it needed for
Phosphorus is extremely necessary for horticultural and horticultural crops during the transition from the phase of active vegetation to the phase of ovary and fruiting. Superphosphate has a well-balanced composition of nutrients in an accessible form, therefore feeding with a mixture has the most beneficial effect on crops:
- promotes the development and growth of the root system, which increases the chances of seedlings to take root and take root in the soil - young seedlings must be fed when planting;
- accelerates flowering and formation of the ovary - with a lack of phosphorus in plants, a lot of barren flowers are noted, and the resulting ovary disappears;
- after the introduction of superphosphate, the fruiting of crops increases, and the palatability of the fruits improves;
- the resistance of plants to diseases increases, superphosphate introduced in autumn improves the adaptation of crops to cold weather;
- after the introduction of phosphorus fertilization, metabolic processes are accelerated and oxidative processes slowed down.
For young plants, phosphorus fertilization is of particular importance - phosphorus contributes to the development of an underground root part, which is very important for seedlings grown in artificial conditions and greenhouse crops. Autumn top dressing of the soil with superphosphate will help grow high-quality root crops. With a phosphorus deficiency, potatoes and beets become stained, and black blotches form inside. Blue leaves of garden crops or home seedlings also indicate insufficient soil fertilization with phosphorus.
How to apply superphosphate
Superphosphate is a versatile complex mixture that can be used as a fertilizer for the soil, as well as for feeding fruit trees and garden seedlings. Fertilizer can be applied to any soil, however, it should be borne in mind that on acidic soil, this dressing is weak. Experienced gardeners fertilize acidic soil with superphosphate only after adding ash or lime - these materials help to equalize the pH of the soil, and thereby increase the effectiveness of superphosphate.
Simple superphosphate is fed by directly introducing it into the holes or rows intended for planting seedlings. The granular preparation can be used to prepare a solution for foliar dressing (spraying). Phosphorus fertilization has some features:
- dry superphosphate fertilize the soil in the fall, since it takes time and a large amount of moisture to dissolve;
- it is better to distribute the granular preparation using a grain seeder, which will provide a more uniform fertilization;
- the main top dressing of the soil with superphosphate is carried out before planting and sowing garden plants (usually when digging);
- bulbous and tuberous crops: potatoes, carrots, beets, radishes, turnips are fed with superphosphate when directly introduced into the holes when sowing, or planting seedlings;
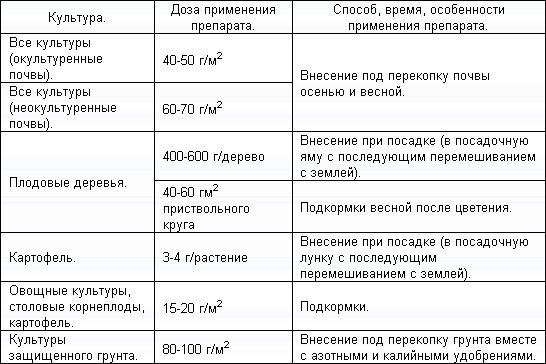
Fertilization rates are as follows:
- when digging the soil in spring and autumn, phosphorus is introduced at the rate of 40-50 g / sq. m - fertile soil is fertilized at the rate of 20-30 g / sq. m;
- for feeding planted plants at the rate of 10-20 g of dry product / sq. m;
- for planting seedlings at 3 g / well;
- horticultural crops are fed at the rate of 40-50 g / sq. m, the depleted soil is fertilized in the amount of 70 g / sq. m
- for adult fruit crops (apple, pear), it is recommended to apply fertilizer in an amount of 300-1000 g / 1 tree, depending on the age of the plants - a solution can be prepared from a dry product, which is introduced into the periosteal circle;
- cherries, plums, cherries are fed with superphosphate at the rate of 200-500 g / 1 tree;
- fruit bushes are fertilized at the rate of 100-200 g / bush;
- for mature seedlings of cucumbers and tomatoes, a solution is used with which crops are watered at the rate of 20 g / one bush;
- feeding of tomatoes is carried out several times per season - they consume 95% of phosphorus during the period of fruit formation, therefore, the bushes are fertilized during the planting of seedlings, then during flowering and ripening of fruits. It should be noted that at the initial stage of growth, nightshade crops do not require intensive phosphorus feeding - for normal development, for the first time they are fed at the rate of 10-15 g / one bush;
- a standard solution for spraying with superphosphate is prepared at the rate of 20 g of double or 40 g of a simple product / bucket of water;
- watering solution can be more concentrated;
- soil for potatoes is fertilized at the rate of 2-3 tbsp. spoons / hole - feeding potatoes with a large amount of phosphorus is necessary for the formation of large and high-quality root crops;
- the soil intended for sowing grain and leguminous crops is fed with phosphorus in the amount of 7-15 c / 1 ha;
- oilseeds require not only phosphorus, but also the microelements present in the preparation - the soil for sunflower crops is fertilized in an amount of 10-20 c / 1 ha.
Cooking the hood
Phosphorus is not a readily soluble substance. Experienced gardeners feed the soil with superphosphate from autumn, so that until spring it dissolves and becomes active under the influence of moisture. But how, then, to carry out spring and summer fertilizing of plants with phosphorus? - this question made gardeners and gardeners look for ways to quickly assimilate superphosphate.
Any fertilizing, including phosphorus, is absorbed by the plants from the soil with the help of root hairs, so it is obvious that for them the only available form of fertilization is a liquid solution. If superphosphate, before being introduced into the soil, is dissolved in water, you get a concentrated extract with a high content of easily assimilable phosphorus. You can prepare the solution as follows:
- Alternatively, the fertilizer can be poured with boiling water and insisted for a day in a warm place (diffusion occurs faster in warmth).
- 100 g of double superphosphate is poured with a liter of hot water, mixed thoroughly, and then boiled for half an hour until the granules are completely dissolved. It is important that only a granular preparation is used to prepare the extract, since the powder contains a lot of gypsum, which precipitates, and thereby complicates the dissolution of superphosphate.
- Then the resulting solution is filtered (the appearance of high-quality feeding should resemble fat milk), and after dilution with water, garden and horticultural crops are fertilized with this suspension.
Phosphorus extract is fed taking into account that 100 ml of fertilizer contains 20 g of pure phosphorus, and this amount diluted in 10 liters of water is sufficient to treat 1 sq. M. soil. The most effective working solution is obtained if liquid fertilizing is diluted in a ratio of 2 tbsp. spoons / 3 liters of water. A large bucket of water will require at least 150 g of the hood. An extract of superphosphate is used to fertilize the soil, and also carry out foliar dressing. The solution is quickly absorbed and has a long aftereffect, therefore it can be considered an ideal option for both garden trees and vegetable seedlings.
Video "Phosphate Feeding"
Informative video, what you need to know about phosphorus plant nutrition.