How to make warm beds with your own hands: popular technologies step by step
Content
Warm bed principle
Compost heaps are familiar to everyone who has been to the village. To put it simply, a warm bed is an organized compost heap that has some of the benefits of a greenhouse and can be made by hand. Dissimilar organic matter is stacked into a large frame in layers. It has a different decomposition period, due to which the crop receives nutrition and heat in the garden throughout the entire growth period.
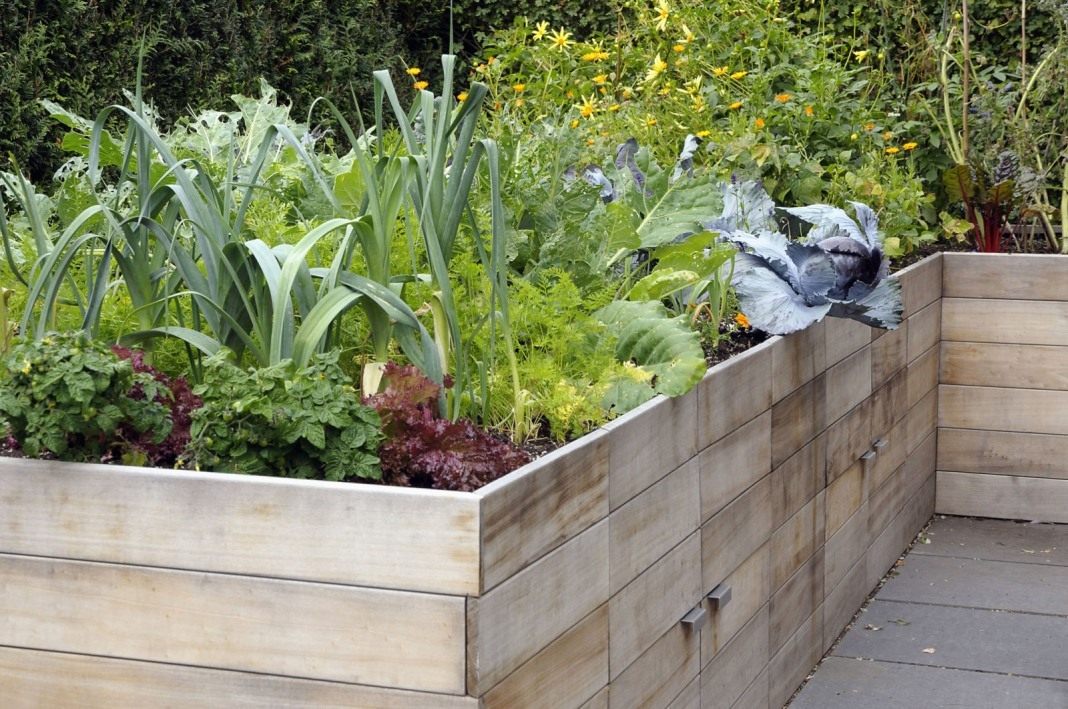

But the manufacture of the garden bed should be carried out strictly according to a proven principle. Otherwise, mold and unpleasant odors may appear. There is a risk of multiplication of pathogens of various diseases.
Compliance with the basic rules will help prevent errors:
- The substrate should consist of large, coarse-structured, long-decaying waste, which will perform a drainage function and provide adequate air exchange. You can use branches, stems of large plants, wood scraps. The main thing is that the layer should be loose, about 40 cm high.
- The raw materials in the garden should always be moderately moist. The soil in such a “smart” garden should always remain moist and not dry out.
- The filling of the bed should consist only of waste from healthy plants that have not been affected by pests and diseases.
The optimal components of the trench can be the following layers (from the bottom to the top): parts of a bulky material (hemp, large branches, etc.), a paper layer (newspapers, old damaged books, cardboard), parts of a shrub, shredded shoots, foliage, compost and land.
A warm bed protects the plant from freezing the soil, so that crops can be planted and harvested much earlier or later (from 2 to 3 weeks). The plant in such beds can withstand the first and recurring frosts, temperatures up to -5 ° C. Plants and fruits grow and develop healthier and stronger, and the yield increases.
The type of soil and the depth of groundwater are practically irrelevant - the culture is protected by drainage layers and receives top dressing from organic matter.
Types of warm beds
The main thing in organizing a warm bed is adherence to the principle, and you can choose any shape. You need to focus on the features of the area where the vegetable garden will be located, and on climatic conditions.
High
This variety is great for areas with excess moisture: flooding in the spring, a lot of precipitation. The manufacture of such an option begins with the selection of a suitable material for the frame-box. It can be wood (larch), brick, stone and metal.Size - from half a meter in height, a meter and a little more in width. In the greenhouse, the width is made half as much.
The frame box is filled with soil and organic matter and is abundantly moistened. In the spring, the structure is covered with a film to speed up the course of biological processes. For the winter, cover with a dark film so that weeds do not germinate.

Recessed
This option is a dug ditch, from which sod and earth are removed and organic matter is filled up. The top level of the bed can be on the same level with the ground or slightly rise. Here, the composition of the soil plays a role in the choice of the first layer: with clay soil, coarse sand is poured onto the bottom, with peat - sawdust.
Combined
The combined version is a complex of the two previous types. But at the same time the ditch is dug shallow and the height of the sides of the box is halved.
Organic matter attracts rodents, so you should take care of the protective layer, which you need to lay out the perimeter of the garden. For this, it is recommended to use a fine-mesh metal mesh.
Bed-hill
A kind of high bed, which allows you to save on the frame (it is simply not used), and the sowing soil is twice as large as the base. Organic components are simply laid out on the soil, giving them the shape of a long, but not wide hill, the edges of which are rounded.

Advantages and disadvantages
Agrotechnical measures must be carried out regardless of the type of garden, the question is in their frequency. And although such beds need more frequent watering, you can save time and energy for feeding. Also, the disadvantages include physical labor, which will be needed in the construction of structures. But this is also relative for lovers of housekeeping. But the material costs for the box and other details should be taken into account.
But the advantages of such beds, of course, are more:
- no feeding is required, which allows you to get an environmentally friendly product and save on the purchase of fertilizers;
- simplified care scheme;
- there is practically no need to use fungicides and insecticides for plant treatment;
- you can use improperly growing or excess vegetation after pruning;
- protection of plants from temperature extremes and excess moisture;
- mulch regulates air exchange and slows down the process of moisture evaporation;
- curbing the growth of weeds;
- you can convert a garden bed into a greenhouse or greenhouse.
Video "Advantages and disadvantages of high beds"
This video tells about the peculiarities of growing cultivated plants in warm beds.
Where and when is it better to make warm beds
The principle of operation of the beds allows you to arrange them both outdoors and in a greenhouse. But at the same time, you need to take care of lighting for at least 6 hours a day. Also, experienced gardeners are advised to arrange the beds from north to south.
The planting of the beds can be done in autumn and spring. In favor of spring time - activation of biological processes. In the fall - more free time and organic residues after harvest.
Self-production of a warm bed
Gardeners willingly share their experience and nuances of making and arranging such mini-gardens. The step-by-step instruction consists of a number of mandatory steps.
Preparatory work
This stage includes all organizational aspects. You need to think about what you are going to plant, and decide on the number of beds. Then you need to choose a well-lit area, and preferably not sunshine, but diffused sunlight. Also, the site must be protected from drafts and strong gusts of wind.Next, you need to take care of the material for the structure and its filling.
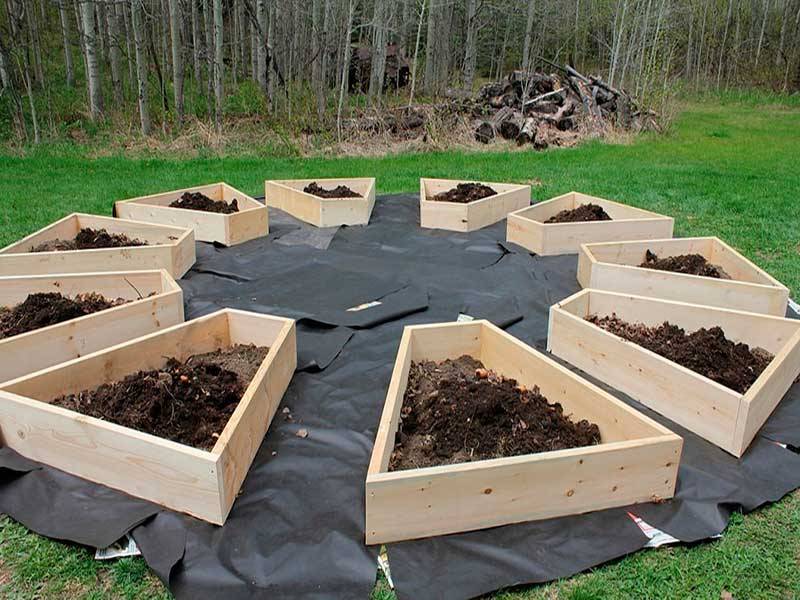

Correct stacking of organic layers
Above, we have listed the optimal installation option and the composition of organic layers. But it's pretty tricky. Therefore, they are more often limited to this scheme:
- The bottom is large wood. Moreover, the larger the part of the wood, the longer the bed will last. These can be tree stumps, branch cuttings, etc.
- Fine organic matter: plant stems, shrub shoots, straw, leaves, grass, paper.
- Growth stimulant. For this layer, manure or compost is used, which is covered with garden sod, located with the roots upwards.
Temporary warm bed device
Temporary beds are used for growing seedlings. They are settling on a buried type. However, the trench is not dug as deep. Such a ditch is filled with organic matter that has the ability to quickly rot or compost. After organic matter is covered with soil and mulch. For the winter, you can sow podzimny green manure.
Permanent warm bed device
A permanent warm bed is built according to the classical principle in one of three options: high, recessed or combined.
High beds are most often equipped on infertile soils, and trench beds - like a mini-greenhouse.
What to plant in a warm garden
The planting pattern depends on the composting processes. Therefore, it is important to know not only what to put, but also when:
- The first year is the maximum level of nutrient saturation and intense heat production. You can plant cucumbers, zucchini, pumpkins.
- The second year - there is still a lot of food and heat. You can continue to plant cucumbers and zucchini, as well as tomatoes and cabbage.
- Crops that accumulate nitrates are not recommended to be planted in the early years.
- The third year - there are still enough reserves for tomatoes, peppers, beans. You can start planting potatoes and beets.
- Fourth year - only greens and peas can be grown without feeding.
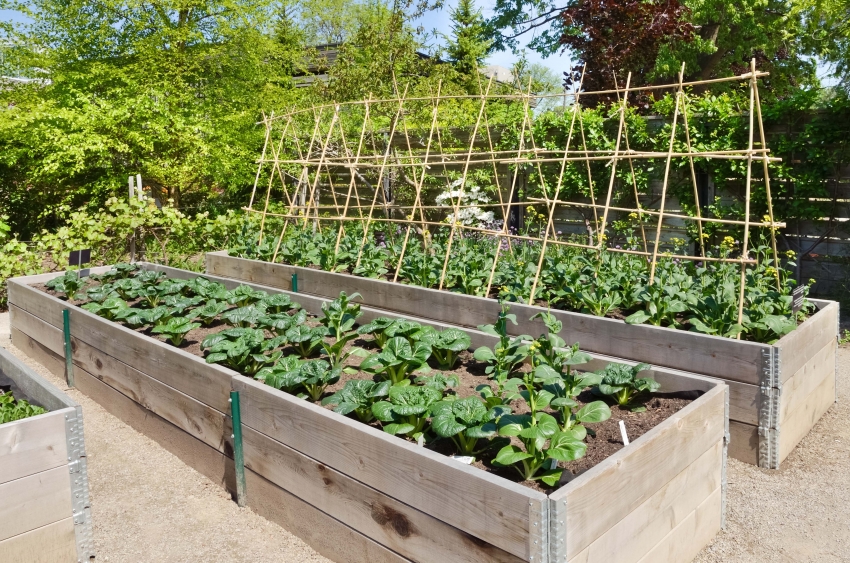

Tips from experienced summer residents
Experienced gardeners do not advise throwing the soil out of a warm garden bed when it has served its purpose: after 5-7 years it will turn into an ordinary fertile soil that can be used in the garden. Also, you should not save on material for arranging the garden and carefully check the components for infection with diseases or pests.
If working in the garden is a joy for you and there is an opportunity to spend a certain amount for a future positive result, we advise you to definitely try the technology we are describing. After all, you will not find a better advisor than your own experience.



