The advantages of growing decorative curly honeysuckle in the country
Content
- 1 History and description of the plant
- 2 Types and varieties of decorative curly honeysuckle
- 3 Video "Honeysuckle climbing in the garden"
- 4 Planting rules for curly honeysuckle
- 5 Features of care and reproduction
- 6 Diseases and pests of culture
- 7 The use of curly honeysuckle in garden design
- 8 Reviews of summer residents
History and description of the plant
Wild plant varieties have chosen the woodlands of Western and Central Europe, and are also found in African and Asian countries.
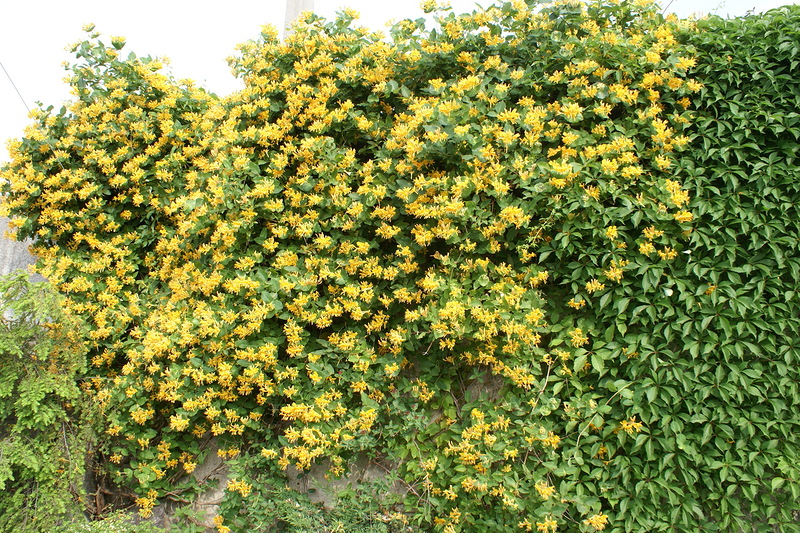

Popularly, climbing honeysuckle is often called wolf berries - rich, red or yellow, but inedible fruits are formed on the branches.For the first time the culture was described by the famous botanist Karl Linnaeus, later (in the 18th century) a more detailed description was given by the scientist from Russia Stepan Krasheninnikov. In the south of our country, in natural conditions, the plant no longer occurs, taking an honorable place among horticultural crops.
Here is a botanical description of the decorative culture:
- Grows in the form of erect, climbing or creeping shrubs.
- The flowers are always massive, the color varies depending on the variety. There are plants with pink, red, yellow, orange and white flowers.
- Inflorescence in the form of a bowl, from where a corolla in the form of a tube, consisting of 5 equal lobes, peeps out.
- The pistil is oblong, each flower contains a group of stamens.
- Fruits in berries, the color of which also varies from cultivar to yellow, blue, black or red. On a branch, they are formed in pairs.
About 200 types of crops have been bred by gardeners; more than 50 varieties are in demand in Russia. About a fifth of the species have edible fruits.
Types and varieties of decorative curly honeysuckle
Cultures are distinguished by their appearance into groups:
- low trees;
- shrubs;
- curly (climbing, weaving) vines.
The planting of the latter is more often used by summer residents to decorate the site. Braiding with lianas, whose flowers shimmer with all shades of the rainbow, a building or a fence, you can transform the landscape of even a nondescript territory.
For our climate, gardeners recommend several varieties that take root well in adverse conditions and do not require special care:
- Honeysuckle. Perennial, foliage falls off in autumn. It grows up to 6 m. Flowering time - mid-May, duration - 20 days. Flowers are replaced by green fruits, which then turn red. Frost resistant.
- Brown. Blooms twice over the summer, in early July and late August. The buds are deep red or carrot-colored. Recommended for planting in open, but protected from drafts, photophilous. The culture has a weak resistance to cold, so it became widespread in the south and in the central regions.
- Henry. Foliage drops partially. Medium-sized in comparison with other species, the stem stretches up to 2.5 m. Vegetation period: July. The flowers are scarlet and have a rich smell.Fruits in September with black berries.
- Serotin. It stretches for 4–5 m. The foliage falls off. Flowering earlier, long-term. Flowers form capitate inflorescences (up to 30 pieces).
- Evergreen doze. The most frost-resistant species. Flowering occurs at the end of May. Inflorescences are tubular, purple with a yellow core. From June to October it bears fruit with red berries.
- Bakchar giant. Edible variety. Tall (up to 2 m), branched crown, dark foliage, picturesque. The fruits are massive, oblong, up to 5 cm, weight - 2.5 g. Up to 4 kg of harvest is harvested from the bush.
- Graham Thomas. Evergreen, frost resistant. It blooms with creamy yellow flowers from June to September. Fruiting from July to October. The fruits are poisonous.
- Graham Thomas
- Bakchar giant
- Evergreen nap
- Serotin
- Henry
- Brown
- Honeysuckle
Video "Honeysuckle climbing in the garden"
In this video, experts talk about the rules for planting and caring for an ornamental crop.
Planting rules for curly honeysuckle
For sowing crops, two methods are suitable - by seeds and with the help of seedlings. The first is difficult and time-consuming, therefore it is rarely used. It is easier to propagate seedlings, you just need to purchase high-quality specimens.
Choosing a place on the site
In addition to its decorative appearance, the plant also has a pleasant smell. For many owners, this is an important factor when choosing a suitable location. It is better to plant the crop near recreation areas.
To bloom profusely, a culture needs sun. However, some forest varieties of honeysuckle prefer shady areas, so they grow better under a dense tree crown. Curly varieties are planted near structures (arches or fences) that need to be decorated.
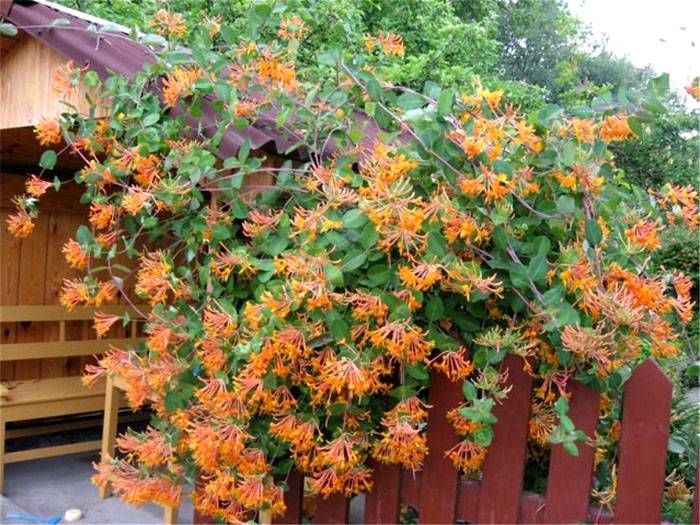

Preparation of soil and seedlings
The soil is selected with a reaction in the range of 5.5–6.5 pH. Lime is added to the overly acidic soil and dug up. Be sure to get rid of weeds, after which organic and mineral fertilizers are applied.
The rules for the selection of planting material:
- Buy in special nurseries or from reliable gardeners.
- For early flowering, seedlings of 2-3 years old are chosen.
- Roots and shoots must be free from defects, flexible, free of dried out areas. Shoots with buds are obligatory.
- It is not scary if the bark peels off - this is characteristic of all varieties of culture. It is better not to take a weak seedling.
It is recommended to purchase three or more varieties for further propagation. Cross-pollinated honeysuckle, therefore it is desirable that there are more pairs.
It is better to buy seedlings in plastic containers, immersed in a ready-made lump of soil - this way you will avoid damage to the roots during transplantation. But when planting in early spring or fall, leave the root bare.
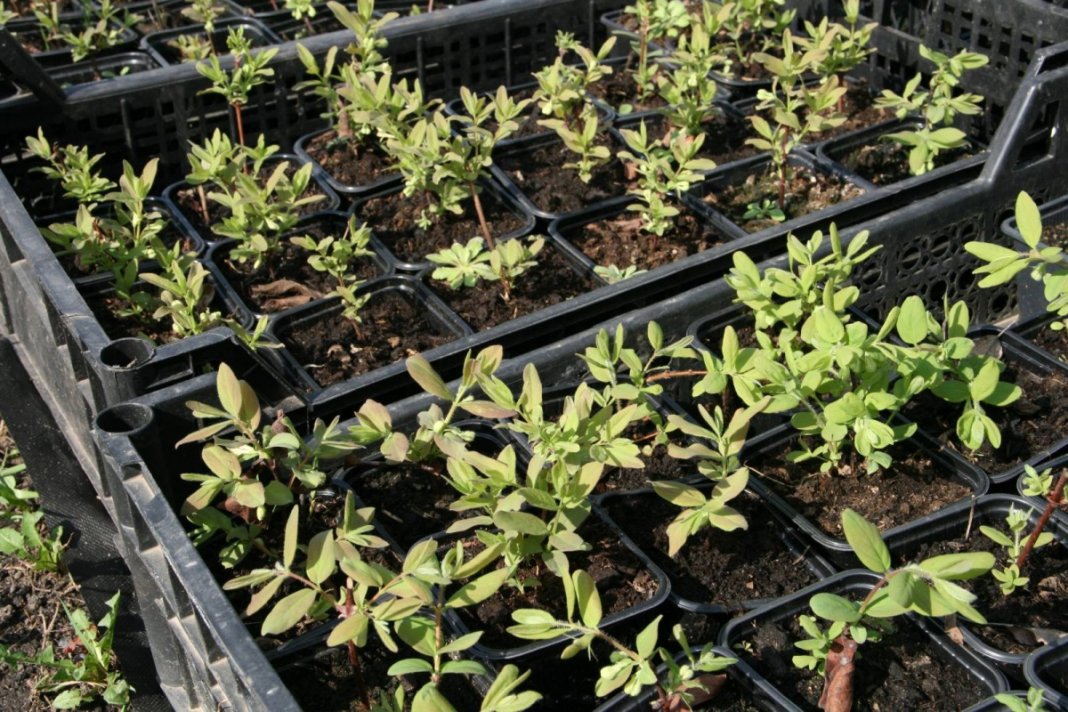

Landing technology
Recommended landing dates:
- late April - early May: the plant will have time to take root;
- end of September: the root system slowly forms throughout the winter.
The landing technology is as follows:
- 3-4 days before sowing, holes are dug under each bush in increments of 1 m for low-growing crops and 2.5 m for tall crops.
- The bottom is drained by pouring a layer of fine gravel, expanded clay or brick fragments.
- Pour a layer of fertile soil. It is bought in a specialized store or prepared independently: 2 buckets of compost are mixed with 1 kg of wood ash and 50 g of superphosphate. For sandstones, stir in a little clay.
- A couple of hours before disembarkation, the fossa is abundantly moistened.
- The seedling is placed in the center, the root is buried with an earthen substrate, making sure that the root collar remains at the surface. The land around is watered several times. As the earth will settle, later it is filled up and re-moistened.
- It is advisable to mulch the root circle with needles, sawdust or peat. The mulch will maintain the desired moisture and protect the roots from frost.
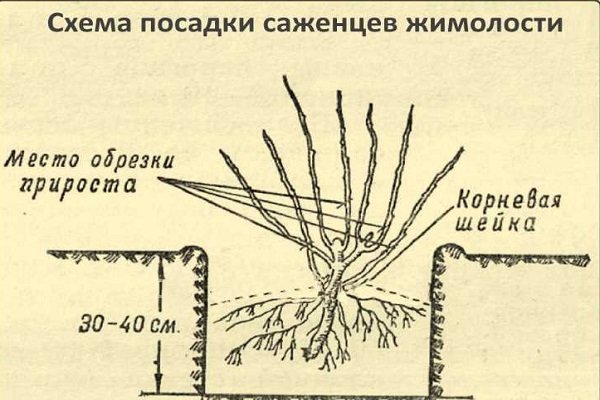
The transplant is carried out when there are no flowers on the honeysuckle, that is, in late autumn or early spring.The culture is transplanted together with an earthen clod so that the plant feels more comfortable in a new place.
For successful growth in height, the vine must cling to the supports. It can be:
- building wall with guide cords;
- gazebo or arch;
- lattices, nets, trellises installed vertically.
Features of care and reproduction
Honeysuckle soon begins to sprout, stretch in all directions, clinging to the supports and taking root. At this stage, the gardener is required to maintain growth at the proper level and from time to time prune excess branches.
Preservation of soil moisture
Moisture is essential for normal plant growth. Agricultural technology assumes the following frequency of watering:
- twice a week on hot days;
- once in cloudy weather.
It is impossible for the soil in the root zone to dry out - the fruits will form small, dry and bitter. Excess is also harmful - stagnant moisture contributes to the development of varietal ailments, root rot.
Top dressing for abundant flowering
Additional feeding enhances growth. Several types of fertilizers are used:
- Mineral is applied shortly before flowering, providing massive inflorescences with energy.
- Shop complex compositions are introduced during the active growing season.
- Wood ash is poured under each bush in late autumn.
- Humus and mullein infusion are added in early July.
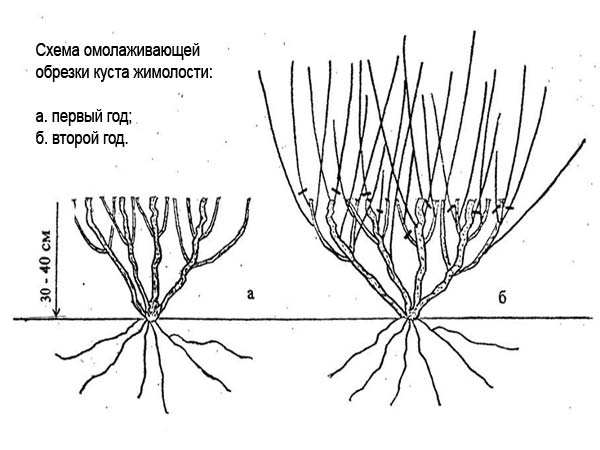
Shrub formation
Periodic pruning allows you to give the shrub the desired shape. The rules are as follows:
- To prevent the bush from growing up, cut off the top. As a result, new shoots appear on the sides, enhancing the overall bushiness and splendor.
- In spring, sanitary pruning is performed, at the same time shortening live shoots by 25-30 cm.
- The bushes are thinned out, reducing the thickening of the crown.
- When the Caprifoli shrub is formed, pruning not only gives the vines a shape, but also rejuvenates the shrub.
Reproduction methods
For this, two methods are used:
- Layers. The procedure is carried out in early spring, as the snow melts and the earth warms up. Choose a strong branch and bend it down. The layering is pinned to the ground with a bracket or pressed down with a brick. During the season, the branch will take root, in the fall the young seedling is separated from the mother bush, dug up and transplanted to a new place.
- Cuttings. Reproduction takes place in July. Cuttings with a couple of intact internodes and several leaves are cut from the bush. The cuttings are placed in a greenhouse, which is made from a plastic bottle, by cutting off the bottom. Cover the stalk by burying the bottle with the cut edge into the ground. The neck is left open for air to enter.
Freeze protection
Most popular varieties tolerate winter frosts well. Even if individual fragments freeze slightly, new ones quickly grow with the arrival of spring. In late autumn, it is recommended to mulch the root areas of the culture. It is imperative to cover the honeysuckle with an agro-bloom.
In the middle lane and the Moscow region, the plant is removed from the support. Vines are laid out on leaves, protruding shoots are pressed to the surface with holders. Cover with coniferous spruce branches, foil.

Diseases and pests of culture
Cultivated honeysuckle has strong immunity, rarely gets sick and is not attacked by pests. But in the early years, young shoots are weakened, so their condition must be monitored.
The plant is attacked by insects. The most harmful of them:
- leaf roll;
- smoky moth;
- honeysuckle mite.
Varietal diseases - viral and fungal - are dangerous to the culture. Powdery mildew becomes a frequent ailment. Specialized insecticides help against pests, but a plant affected by fungi and viruses cannot be cured. The best way out is to dig a bush and burn it so that the infection does not spread to neighbors.
Gardeners recommend timely preventive measures to prevent the formation of larvae and adult aphids. The measures are as follows:
- the trunk circle is sprinkled with granular superphosphate or lime;
- by winter, shoots are sprayed with a 5% urea solution;
- periodically carry out treatment with drugs "Lepidocide" or "Bitoxibacillin".
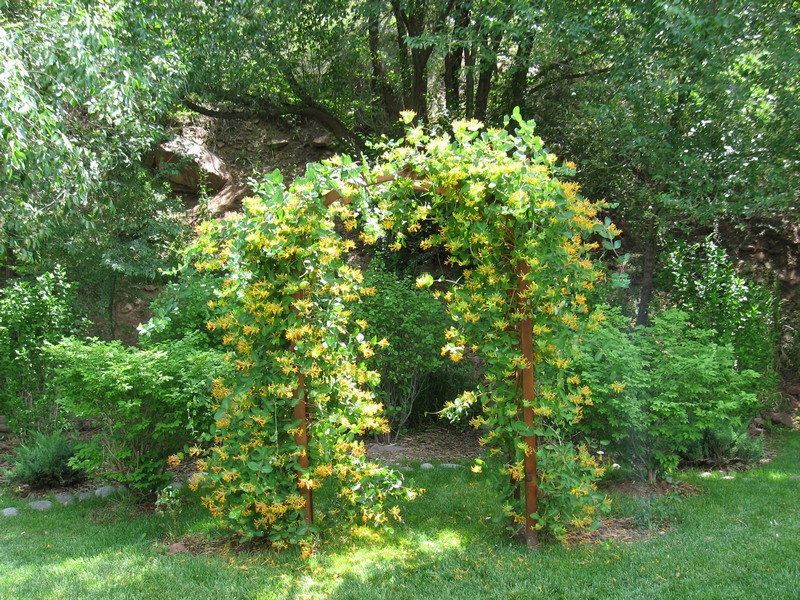
The use of curly honeysuckle in garden design
Since the culture is planted for decorative purposes, fences, walls, arched and other garden structures are decorated with it. You can plant a bush separately and in a group, but with plants of the same species - the short flowering period does not allow combining honeysuckle with other lianas. It is well grouped with climbing crops - hops, girlish grapes.

Reviews of summer residents
“I planted the Nymph variety near the house. The berries are bent, sweet ones hang on the branches and do not crumble. I take off one and a half kilos from the bush. "
“We used to live in Siberia, they used to pick honeysuckle berries in the taiga. Having moved to Moscow, they planted a garden culture on the site. The fruits are blue, oblong, tasty, but with a bitter taste. "
Moderate grooming, loosening and infrequent pruning is enough for bush honeysuckle to grow beautifully on the site. Over the years, culture has carefully masked unsightly objects. An ornamental fragrant plant that wraps around the gazebo allows owners to feel as if they are in the bosom of wildlife.







