What the amaranth plant looks like: common species and varieties
Content
Description and characteristics of amaranth
All plants belonging to the genus of the same name have a similar appearance. As a rule, these are annual, sometimes perennial grasses with a powerful branched stem, wide leaves and large spike-shaped inflorescences hanging under their own weight. The height of plants, depending on the species, varies from 0.7 to 2.5 m. The stems can be smooth or pubescent. Leaves are oblong-ovate or slightly pointed, with noticeable veins.
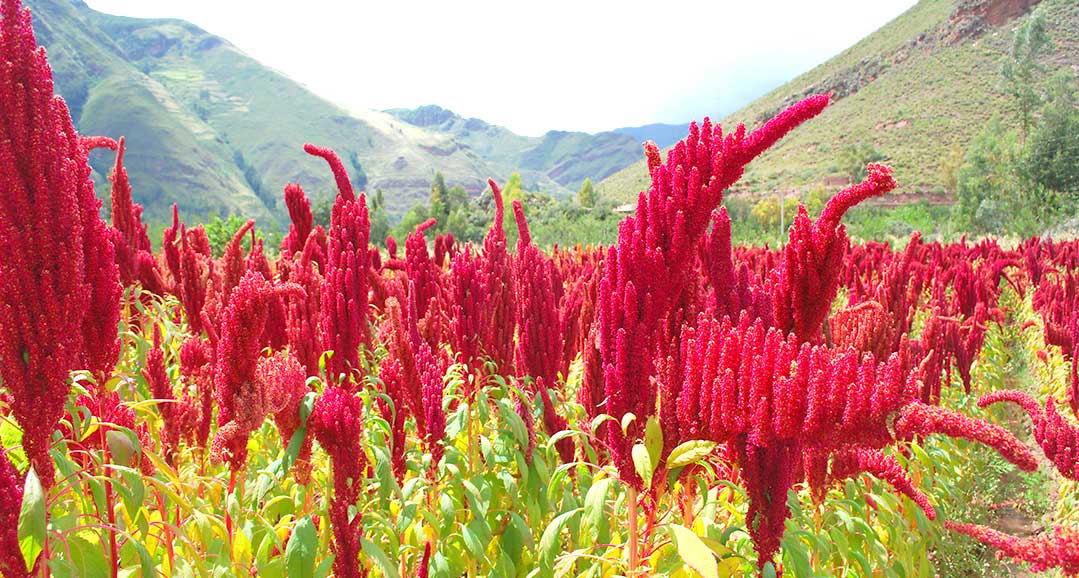

The squid blooms with long inflorescences of red or purple, less often light color. A huge number of microscopic seeds ripen in flowers, which spill out of the seed pods on their own. One inflorescence can contain up to 500 thousand of them, while they are so small that up to 2.5 thousand pieces fit in 1 g.
Culture grows everywhere, as it is completely undemanding to the composition and acidity of the soil. Wild species are found on neglected areas, roadsides, some of them inhabit vegetable gardens and fields, where they are considered malicious weeds. The name amaranth translates as "unfading flower". Lush panicles really retain their appearance for a long time and dry easily, which allows them to be used in bouquets at any time of the year.
Chemical composition and useful properties
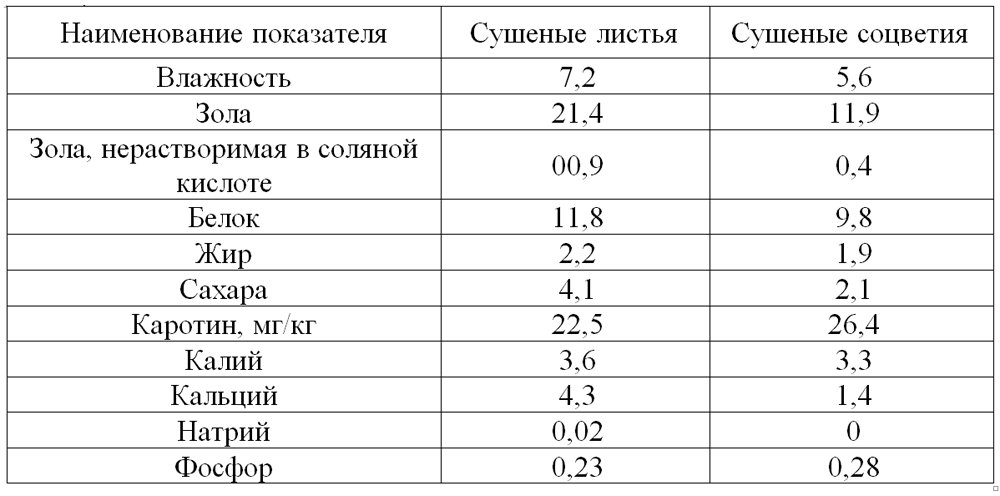
It is not for nothing that the ancient peoples considered the shchiritsa a source of health. Scientists have identified a whole range of health-promoting substances in it. All terrestrial parts of the plant contain a large amount of easily digestible proteins, fatty and unsaturated acids, vitamins C, E, PP, group B, a unique set of micro- and macroelements.
The healing properties of the plant are due to the presence of a special alkaloid, isolated only from the shirin, as well as a set of other biologically active components: polyphenols, ethers, pigments, triterpenes, steroids, several groups of flavones with high antioxidant properties.
Thanks to this composition, the plant has a positive effect on the body:
- strengthens the immune system and protects against colds;
- has anti-inflammatory and antitumor effects;
- regenerates the skin;
- restores the body after chemical and radiation exposure;
- improves cardiac activity;
- leads to normal metabolism;
- lowers sugar levels;
- has an antibacterial and hemostatic effect;
- strengthens bone tissue, preventing the development of osteoporosis, arthritis.
It is recommended to take broths from the squid for hypertension, obesity, neuroses, diathesis, pathologies of respiratory dullness, with prolonged menstrual bleeding in women. Externally, decoctions are used for eczema, dermatitis, for the treatment of problem skin. Fresh juice from chickweed is incredibly useful - in terms of its composition and properties, it is able to replace mother's milk for newborns.
Cooking use
Seeds, leaves and young stems of the plant are of culinary value. Greens are added to salads and soups, blanched or stewed like spinach. Shirin seeds are a raw material for the production of flour, from which delicious bread and other pastries are made. They are also used to prepare healthy vegetable oil, and in some countries, for example, in Peru, beer is brewed.
Unprocessed seeds are used in cereals and even desserts. Due to the high level of starch, they swell quickly, giving a dense consistency to the food. Since it is very difficult to chew the seeds due to their small size, they are mixed with chopped dried fruits and added to smoothies.
In ancient times, bread from the seeds of the shpitra was considered a source of longevity. The aromatic pastry did not dry out for a long time and was a valuable protein product.

Application in cosmetology
Oil is considered the most valuable in cosmetology. The active ingredients in its composition have a positive effect on the condition of the skin: they smooth it, gently cleanse, moisturize and nourish it. In home cosmetology, it is recommended to use oil to cleanse the skin from acne and rashes, improve the condition of nails and hair.
When treating hair, oil is rubbed into the scalp, a few drops are added to rinses. You can also prepare herbal decoctions for rinsing. For face care, the product is used in its pure form and as part of masks, the recipes for which are very simple:
- for dry skin, mix oil and honey (1 tablespoon each) with raw yolk;
- for skin prone to rashes, the following composition is suitable: 1 tsp. fresh lemon juice, 2 tbsp. l. oil and the same amount of orange juice;
- a mask of oil and any cosmetic clay in a 1: 2 ratio has a cleansing effect.
Harm and contraindications for use
The only contraindication to the use of shirin products is individual intolerance and a tendency to allergies. In addition, excessive use of medicinal decoctions can aggravate the condition of hypotensive patients and people with pancreatitis and cholecystitis.
Video "The benefits of amaranth"
This video presents the beneficial and medicinal properties of the plant.
Amaranth species and varieties common in nature
The genus Amaranthus unites more than 100 species, but no more than a dozen are found in the nature of central Russia. The rest are cultivated specifically as vegetables, fodder and ornamental crops. Let's consider the most common types.
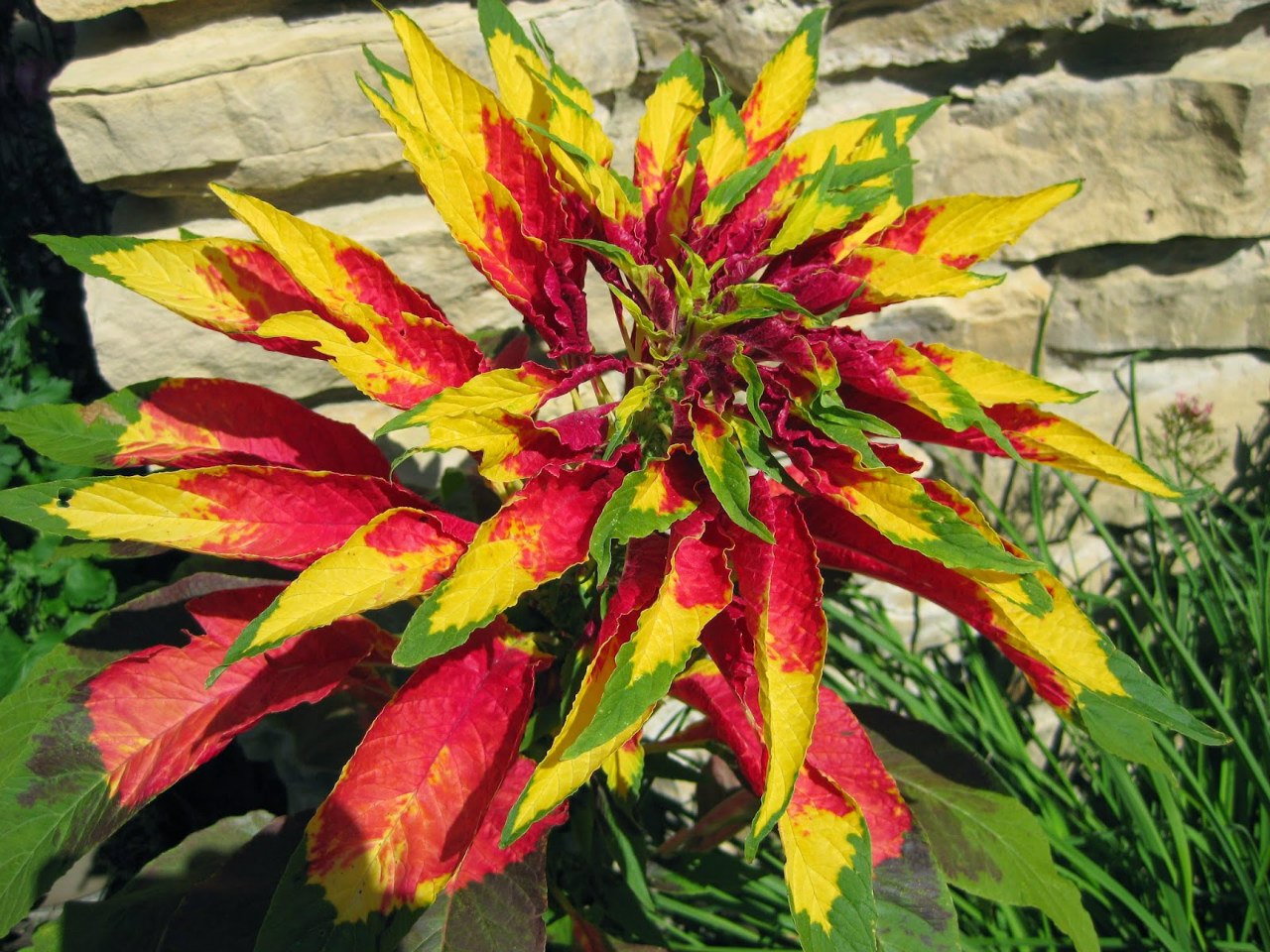
Tricolor
Very bright, decorative annual, reaching a height of 1.5 m. The lower leaves are green, the top is decorated with a "cap" of elongated variegated leaves of yellowish and purple colors. The culture is cultivated mainly for decorative purposes.
The best varieties of this type:
- Illumination is a shrub 60-70 cm high with large foliage and a bright top in bronze and red tones;
- Willow is a shrub with a pyramidal crown and elongated bronze leaves in the upper part.

White
A low ornamental shrub blooming with long hanging "earrings" of light beige, almost white. Leaves are bright, greenish-lemon color. When they die off, the inflorescences become tumbleweeds.
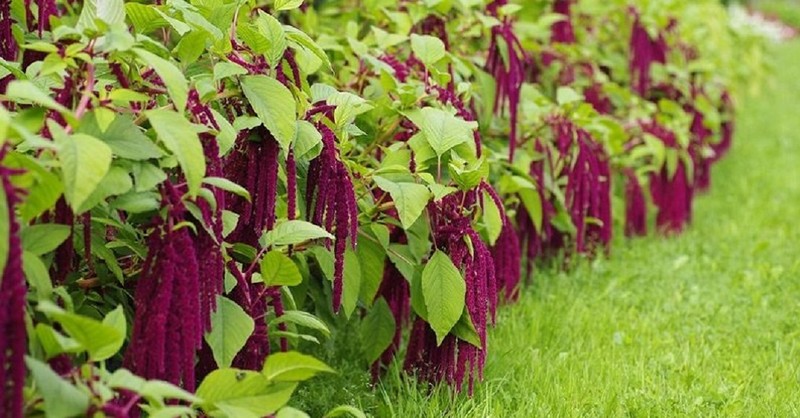
Red
It is cultivated as an ornamental and potting culture. A shrub up to 1.5 m high is distinguished by bright foliage of a rich burgundy color and red, several tones lighter, apical inflorescences.
Thrown back
Wild and the most "modest" representative of the genus - it has neither bright leaves, nor beautiful inflorescences, it is considered a weed. It grows to an impressive size. It has a long tap root that is difficult to break out of the soil. It blooms from June to August with inconspicuous green inflorescences.
- Thrown back
- Red
- White
Panicled, or crimson
A fast-growing annual, reaching a height of 1.5 m. Large green leaves with burgundy veins and red paniculate inflorescences give the plant a bright appearance.
Popular varieties of this species:
- Roter Dam is a low (up to 50 cm) bush with wide leaves of a light burgundy hue and burgundy inflorescences;
- Hot Biscuit is the highest representative of the paniculate species, reaching 1.5 m. The leaves are green with bright burgundy veins, the inflorescences are fiery red.

Caudate
An ornamental annual with strong branched stems reaching 1.5-2 m. Leaves are green with burgundy veins, inflorescences are complex, consisting of many thin crimson, brownish, sometimes purple or light "tails". Blooms from early summer to October. Varieties of this type:
- Grunschwanz - a short bush with scarlet inflorescences;
- Albiflorus is a bush with beige buds.

Spicate
This species is considered a weed. The shoots are strong, reddish at the bottom, green at the top, reaching a height of 3 m. The leaves are glossy, about 15 cm long. The weed blooms with green inflorescences in mid-summer.
Zhmindovidny
Herbaceous annual with strong, well-branched and lodging stems. It looks completely different from its relatives - the leaves are glossy, rounded-oval, dark green in color. Inflorescences are small, formed in the axils of the apical leaves, they are inconspicuous in appearance.
Sad, or dark
Heat-loving culture with lanceolate foliage of dark emerald color. Inflorescences, large, deep burgundy. The variety is often planted in flower beds and is used in floristic compositions.
- Sad, or dark
- Zhmindovidny
- Spicate
Vegetable
Representatives of this species are characterized by a high content of nutrients and a short growing season - young shoots can be used for food after 60-70 days.
Popular varieties:
- Opopeo is a powerful shrub with bronze-green leaves and red buds;
- Strong is an early maturing crop with massive green leaves and brownish clusters.

Amaranth is a promising and very prolific crop. Having planted the plant once, it will be quite difficult to remove it, since the weed reproduces well by self-sowing. But this is a plus, because the shiritsa can be used in many areas, while it will become a decorative decoration of the site.






