All about planting and caring for freesia at home and outdoors
Content
Description of freesia
This is a perennial crop of the Iris family. Subject to the rules of agricultural technology, it normally takes root in an open-air flowerbed or in a flowerpot on a loggia. Freesia, whose homeland is South Africa, is accustomed to the tropical climate, so the grower needs to try to create the necessary comfortable conditions for the flower.
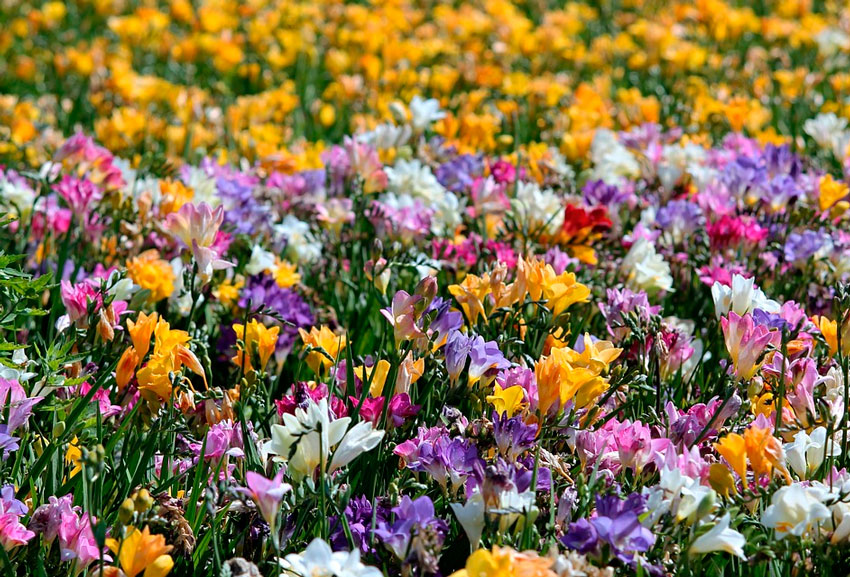

Botanists classify the flower as a perennial herbaceous tuber crop. Here's a short description:
- The leaves are thin and elongated.
- The stems, together with the foliage, grow from a common base.
- Bell-shaped petals that look like porcelain. Some varieties have a solid color, others have pink, purple, white, yellow, lilac, red or blue.
- The flowers are small, formed into massive brushes of 5-10 pieces. They have a pleasant lily of the valley scent. There are terry and semi-double varieties.
In the century before last, picturesque and delicate freesia was considered the flower of monarchs; it was bred in the royal greenhouses for aristocrats. Nowadays, thanks to the efforts of breeders, culture has become a frequent visitor to city flower beds and squares.
Interesting species and varieties with photos
In total, the International Flower Base lists 16 naturally occurring perennial species, combining 200 varieties. Some of them are popular with us.
Freesia armstrongii
Low grade, the stem grows up to 65 cm. The growing season falls in May-June. Forms strong branching stems. The buds are pink and red.
Freesia hybrid (Freesia hybrida)
The result of hybridization of varieties f. refracta and f. Armstrongii. More massive and richer in color than the parents. The variety is highly branchy. Tall, the stems are 1 m long. The inflorescences are large, of different shades. Often grown in a pot.
Representatives:
- Ballerina;
- Rose Marie;
- Pimperina.
Freesia white, or refracted (Freesia refracta)
One of the smallest varieties, the stem is thin, it grows up to 40 cm. It opens earlier than its relatives. The inflorescences seem to be terry due to the densely spaced white or golden buds.
- Rose Marie
- Armstrong
- Ballerina
- White
Video "Growing freesia in the garden and at home"
After watching this video, you will know everything about growing a flower.
Growing freesia outdoors
A perennial is grown at home, outdoors or in a greenhouse. The difficulties of growing are as follows:
- loves warmth, but not heat;
- needs long-term lighting, but is afraid of sunburn;
- thin peduncles cannot withstand the weight of foliage and flowers, therefore reliable support is required;
- feeding and moisturizing are important, but with an overabundance, the growth of green mass increases, flowering is blocked;
- flowers can be grown in the temperate zone, but the bulbs will not survive the winter, therefore they are dug up in the fall and stored until the next season.
Site and soil preparation
When choosing a landing site, preference is given to the following sites:
- partially in the shade;
- protected from strong winds;
- with loose, fertile soil.

The soil must be drained so that the roots have enough air. At this stage, it is advisable to worry about supporting pegs so that thin peduncles do not break under the weight of large buds. In greenhouses, several nets are used for this:
- the first is pulled horizontally at a height of 20 cm from the surface;
- the second is 20 cm higher;
- the third may be needed for tall varieties.
The mesh cells are selected wide so that the culture grows freely through the supports.
Taking into account the tropical nature of the culture, planting in open ground is planned for the end of May, excluding the risk of late frosts.
Seed planting
The technique is rarely used (only for growing some special varieties). Landing is carried out in a spacious container according to the scheme:
- Seed material is scattered on the surface of the moistened earth, covered with a thin (up to 2 cm) layer of soil, stretched over a film or glass is placed.
- When the first shoots hatch, the planting is thinned out, leaving only the strongest plants.
- In the last days of spring, they are planted in the ground.

Bulb planting
Experts recommend sprouting the sowing bulbs a little at first. To do this, a couple of months before planting the seed:
- examine, getting rid of defective scales;
- disinfected in a solution of "Fundazol" against fungal diseases;
- planted in a small container with peat to a depth of 5 cm;
- keep in a warm, bright place.
At the end of May, they begin to disembark at the chosen place. Pits are prepared according to the rules:
- the width is 3 times the diameter of the bulb;
- depth of about 5–10 cm (the heavier the earth, the less);
- step of 3-5 cm (depending on the size of the bulbs);
- the row spacing is 15 cm.
A handful of sand is thrown into the hole, a layer of fine gravel is poured, 2 tablespoons of wood ash are added. They stick in an onion, add soil, ram it with the palm of their hand. The place is moistened and mulched with peat or coniferous soil. If the soil is too acidic, stir in lime or dolomite flour, achieving a decrease in acidity to a neutral pH.
Care advice
Freesia bushes usually grow up to 40 cm by July, then buds are formed. Flowering occurs in August, lasts until October.
Flowers are periodically fed, fertilizer is applied several times during the season:
- With the emergence of seedlings. You will need a solution of ammonium nitrate at the rate of 20 g per bucket of water.
- Twice a month, they are fed with a potassium-phosphorus solution (20 g of potassium salt and 40 g of superphosphate per bucket of water).
The plant is susceptible to weeds - regular weeding is needed. After watering and rains, the soil is loosened, giving access to air.
The irrigation regime deserves a separate explanation. Freesia especially needs moisture during the growing and flowering season. During this period, plantings should be watered often and abundantly. After the growing season, the number of watering is reduced, then stopped. From time to time, it is enough to spray the leaves with water, increasing the humidity. The procedure is performed in the evening, otherwise the water drops will work in the sun like lenses, leaving burns on the foliage.

Cleaning and storage of bulbs
For the winter, the culture is dug up. You can understand that the deadline has come by the yellowed foliage.Another criterion: the root becomes thinner, drying out into a thread. For verification, a test excavation is carried out.
Cleaning is performed according to the following scheme:
- the yellowed tops are removed;
- the bulbs are dug up and carried to the heat;
- laid out on paper (away from the window), dried for about a week;
- cleaned of dried scales, collected in a cardboard box and hidden until next season.
Store warm (up to +30 ˚C), but at high humidity, so that the material does not dry out (you can put a container with water nearby). A couple of weeks before the new planting, it is desirable to lower the temperature to 12-13 ˚C, and let the material harden in the refrigerator a week before (at +5 ˚C).
Features of freesia agricultural technology at home
It is easier to care for a thermophilic plant in a house or apartment. Low-growing varieties are suitable for the windowsill, such as Anyuta, Tenderness, Purple with a stem height of 20-25 cm. The material is prepared - disinfected, treated with biostimulants. Let's figure out what needs to be done so that the culture emerges in early spring.
Illumination and ground requirements
The prepared container is covered with a drainage layer (small stones), filled with a mixture of sand, peat and turf. The bulbs are deepened by 5 cm. Supports are installed - a wire frame or a lattice of slats. In autumn and winter, daylight hours are artificially increased to 12 hours.
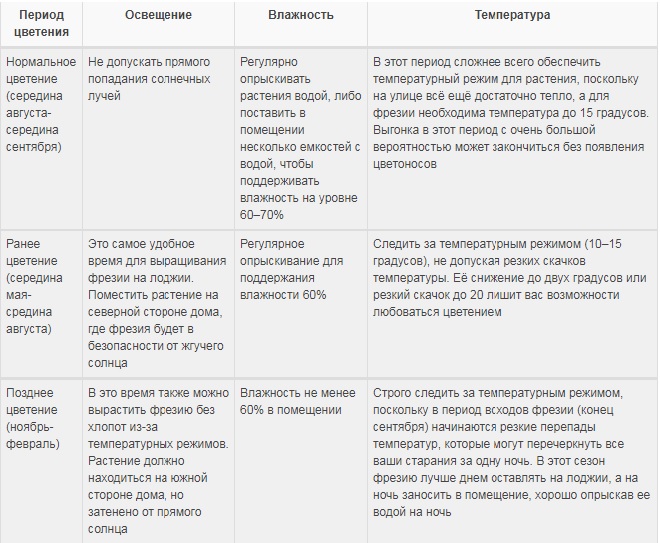
Temperature and humidity
Since the house is heated in winter, the humidity is greatly reduced. The leaves of the plant must be sprayed every day, increasing the humidity.
During winter forcing, they adhere to the temperature regime:
- during the period of emergence of sprouts - about + 10–12˚С, + 6–7 ˚С is possible;
- in the flowering season - not higher than +20 ˚С.
To enjoy the first flowers in winter, the bulbs are planted no later than September.
General rules of care
Until the emergence of shoots, containers are stored in a cool place, do not watered. With the appearance of sprouts, they are transferred to where it is warm and sunny, watered daily, preventing the top layer of the soil from drying out. Top dressing is applied every two weeks. Fertilization is interrupted when the leaves turn yellow and dry.
After flowering, all leaves and peduncles are cut off, leaving only the bulb in the ground. Watering is extended for a couple of months, allowing daughter bulbs to form on the maternal root. After they are removed, treated with potassium permanganate and stored.
Let's explain the unpleasant situations faced by inexperienced growers:
- The plant does not bloom. The room is most likely too warm.
- The leaves of the culture are drying up. The reason is the lack of moisture in the soil and in the air.
- Yellow and brown spots appear on the plant. The flower is either overfed with fertilizers, or it is sunburn.
- There are no shoots. Most likely, the bulbs were not prepared correctly - they were not disinfected, they were not impregnated with a biostimulant, they were stored in improper conditions.

Diseases and pests of freesia
A perennial suffers from the same ailments and pests as other bulbous crops. The threat is posed by:
- thrips;
- aphid;
- spider mite.
For prevention and treatment, crops are sprayed with insecticides and acaricides.
Their infectious ailments freesia are dangerous:
- scab;
- fusarium;
- rot.
Alas, these diseases are not amenable to treatment. If symptoms are found, until the disease is transmitted to neighboring bushes, the affected specimen must be dug up, grabbing a lump of soil, and burned. In order to prevent ailments, the bulbs are recommended to be disinfected in potassium permanganate before storage and planting or to hold for an hour in a fungicide solution (for example, "Photospirin"). It is also important to follow the rules of agricultural technology - competent and timely care reduces the risk of disease to a minimum.
Growing freesias is a complex process, but extremely exciting. But how much joy the pleasantly smelling picturesque flowers will bring to the owners later.




