How to properly prepare clematis for winter
Content
Autumn care
Most perennials in the fall need a number of activities that complete the growing season and begin preparations for winter. So, already from August, nitrogen is excluded from top dressing, otherwise the plants, instead of ripening existing shoots, will begin to grow new ones.
In autumn, plants must be watered abundantly, and if there is no rain, then even twice. Then the clematis are fed, removed from the supports, cut off and insulated. Before winter, the trunk circle is treated with fungicides to prevent fungal diseases next year.
In the ground under the bushes, they usually try to overwinter the larvae of parasites and pests, pathogens of all kinds of diseases. In order not to leave them a chance, it is advisable to process the ground and the lower part of the shoots with iron vitriol (2%) or Bordeaux liquid (1%).
Pruning rules
There are several types of scraps: formative, rejuvenating and sanitary. Autumn pruning combines them all and helps cover the plant for the winter. The best time for her is 2-3 weeks before frost. In different regions, it is held from late October to mid-November.
Young plants of the first year of life are cut at a height of 20–30 cm, leaving only three healthy buds, regardless of the species or variety. This allows not only to properly cover the still weak plant, but stimulates the growth of lateral shoots, due to which a lush bush will grow next year.
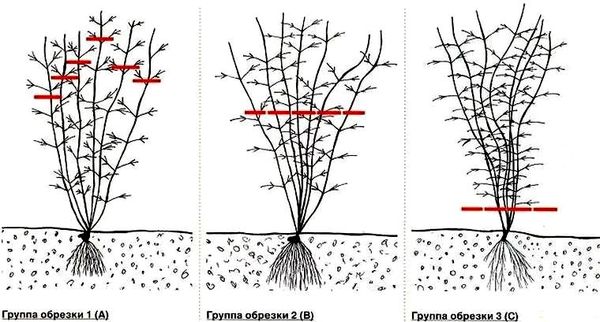
But adult clematis are pruned depending on which shoots the flowers are formed on. On this basis, all varieties are traditionally divided into 3 groups:
- The first includes varieties that form flowers on last year's shoots, for example Biryuzinka, Hegley Hybrid, Cardinal Rouge, etc. Only damaged, diseased or very weak shoots are cut from these plants, and the rest are shortened to 1.5 m.
- The varieties Ball of Flowers, Minister, President, Dawn, Fair Rosamund bloom twice - since the beginning of summer on the shoots of last year, and since July - on the shoots of the current year. Such varieties belong to the second group, they are recommended to be cut at the level of 1-1.3 m from the ground. But experienced growers advise to cut all healthy shoots through one: shorten one to 1.2 m, and the other to 20-30 cm, so that 2-3 buds remain on it. After such pruning, the flowering of the first and second waves will occur at approximately the same height level, which will form a beautiful neat bush.
- The third group united clematis blooming only on the shoots of the current year. These are the Zhakman, Integrifolia, Vititsella groups. Depending on the variety, they are cut in two ways - at a height of 20-30 cm, leaving up to 4 pairs of buds, or almost at the very ground, leaving only 2 buds.
Subsequent feeding
A good preparation for cold weather is feeding with mineral fertilizers containing potassium and phosphorus. Fertilizers are scattered over the entire area of the trunk circle, slightly embedded in the ground, or dissolved with water and poured into a groove made along the perimeter of the trunk circle. Wood ash, scattered under the plants, has proven itself well, which at the same time fertilizes them and repels pests.
Clematis does not like acidic soil, so pine needles and sawdust of coniferous trees used for insulation (simultaneously with scaring away rodents) must be removed in the spring when it is time to disassemble the shelter.
Video "Preparing clematis for winter"
From this video you will learn how to properly prepare clematis for the winter period.
Variety of shelters
The shelter of different clematis for the winter should differ depending on their frost resistance, the degree of pruning, and the region of growth. There are frost-resistant varieties, and there are those that are afraid of even a ten-degree frost. But water can destroy a plant worse than the most severe frost: flooding of the roots during a thaw will bring inevitable death to the plant with the return of frosts. Therefore, to prepare the bush for wintering correctly means pouring a hill at least 30 cm so that it does not end up in a hollow in any case.
The bushes are spud with earth mixed with dry peat, humus, wood ash. Young clematis should survive their first winter well wrapped, regardless of the degree of frost resistance of the variety.
Of course, it is easier to cover short, heavily trimmed bushes. They are huddled high, wrapped with lutrasil or other non-woven material, a frame is erected over them, covered with fallen leaves or covered with spruce branches.
Plants with long shoots are closed according to the same principle, only they need to be covered from above with a hard roof so that heavy snow does not roll over the entire shelter, depriving it of ventilation. After pruning at the desired height, the wires and ropes are carefully untied, with which the shoots were tied to the trellis, the leaves are cut off with scissors, which are hooked to the support for stability.
After that, the plant is wrapped with lutrasil, laid horizontally (having previously hilled the roots, covering the near-stem circle), only not on the ground, but on a pillow, the role of which can be played by a board, polystyrene, spruce branches, a trimmed part of the same bush. It is best to build a frame, cover it with insulating material, put a hard roof on top, and fill the space inside with litter, sawdust or pine needles.
Clematis leaves do not crumble, but they are cut off in the spring. At the same time, they carry out sanitary pruning, untangle the shoots, attach them to the trellis only on one side, otherwise they will braid it too much and it will be impossible to remove it in the fall. It is advisable to place traps for rodents next to the plant or scare them away, for example, mice do not like sharp pine needles.
Landmark on geographic zones
The degree of insulation must correspond to the severity of winter and the climate. So, in the Moscow region and throughout the middle zone, winters are not too harsh, but sharp fluctuations in temperature threaten to destroy the plants if they mate during a thaw or water collects in the shelter. Therefore, flower growers have to air the clematis, and cover them in such a way that they can be easily opened or wrapped up again.
The Volga region is characterized by high humidity. Here the plants need to be hilled high, whole hills should be poured at the bases. Some summer residents cover the ground above the roots with polyethylene, and they shovel earth, peat, sawdust onto it.
The harsh conditions of the Urals and Siberia require more thorough insulation. The abundance of snow will protect against frost, but it is imperative to make a frame and a rigid roof so that it does not sag under the weight of the snow. Such conditions require the cultivation of early varieties, since winter comes quickly, and the shoots of late-flowering clematis do not have time to ripen to frost, which means they may not survive until spring with any cover.
It is very important not to forget about winter care: in frosts, snow should lie on sheltered flowers, during thaws it is necessary to check if water has accumulated under the plant.
If the ground under the shoots is wet, boards, slate, roofing material are placed on it - any material that will help protect the branches from moisture.