Care and review of tomato diseases in the greenhouse
Content
Tomato care
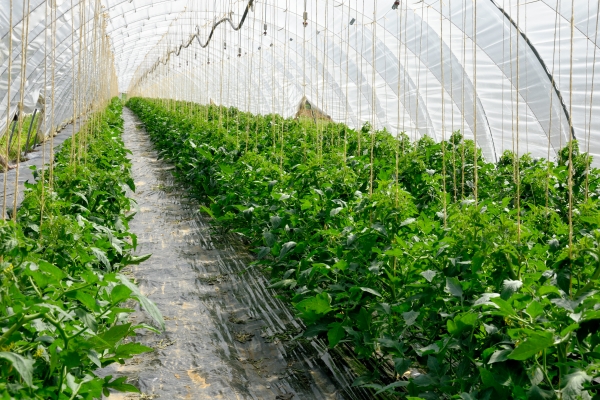
The approaches to growing tomatoes in open ground and greenhouses vary greatly. For planting in a greenhouse, those varieties are suitable that are most adapted to our climatic conditions. The special microclimate inside the greenhouse, proper care of tomatoes have a beneficial effect on the normal growth and development of crops. A greenhouse for growing tomatoes should be quite spacious, have several vents for ventilation, which is especially important for plants during flowering and fruiting. Recently, greenhouses made of modern polycarbonate material have gained wide popularity, in which you can create favorable conditions for growing tomatoes. Tomatoes that appeared in greenhouse conditions with normal care, without the addition of excess fertilizers and growth stimulants, have the same excellent taste properties as those grown in natural conditions.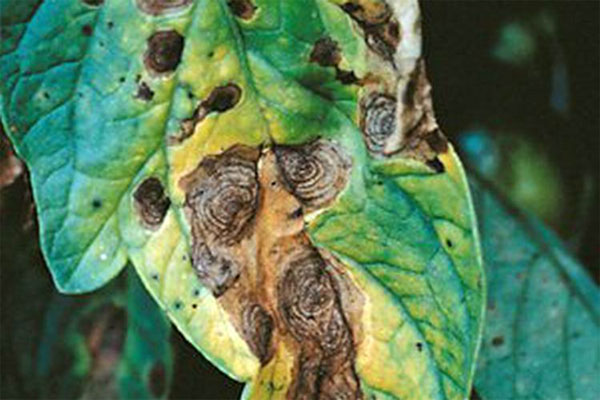
Since tomatoes are very demanding on heat, the room should first of all create the desired temperature, which should be about 22 - 24 degrees. You also need to worry about sufficient greenhouse lighting, because if there is a lack of it, the tomatoes will necessarily develop poorly, their leaves will turn pale, the buds will fall off, and the stems will stretch out. In order to stimulate the good growth of tomatoes in the greenhouse, special artificial lighting is created, as close as possible to the natural one they are used to, which has a positive effect on the quality of seedlings and obtaining a good harvest in the future.
 In early spring and late autumn, it is recommended to carry out gas disinfection indoors, using sulfur smoke bombs for this. Before starting this event, all cracks that will be found in the greenhouse structure must be carefully closed. An important role in the formation of future high-quality tomatoes is played by soil preparation, for which the top layer and the remains of previous plants are removed in the fall, after which they are watered with copper sulfate or Bordeaux liquid. Complex fertilizers are introduced and dug up. After high-quality heated and treated with chemicals seeds are planted in prepared boxes, seedlings will appear from them in due time and after that you can start planting them in the ground and subsequent care.
In early spring and late autumn, it is recommended to carry out gas disinfection indoors, using sulfur smoke bombs for this. Before starting this event, all cracks that will be found in the greenhouse structure must be carefully closed. An important role in the formation of future high-quality tomatoes is played by soil preparation, for which the top layer and the remains of previous plants are removed in the fall, after which they are watered with copper sulfate or Bordeaux liquid. Complex fertilizers are introduced and dug up. After high-quality heated and treated with chemicals seeds are planted in prepared boxes, seedlings will appear from them in due time and after that you can start planting them in the ground and subsequent care.
Two weeks after planting young tomatoes, the soil around them should be gently loosened. After 12 - 14 days, it is necessary to feed vegetables for the first time using peat mixed with humus and sod land. This procedure for caring for plants will enable them to begin intensive growth and development. After waiting another couple of weeks, fertilize the soil with a mixture of humus, turf and peat again.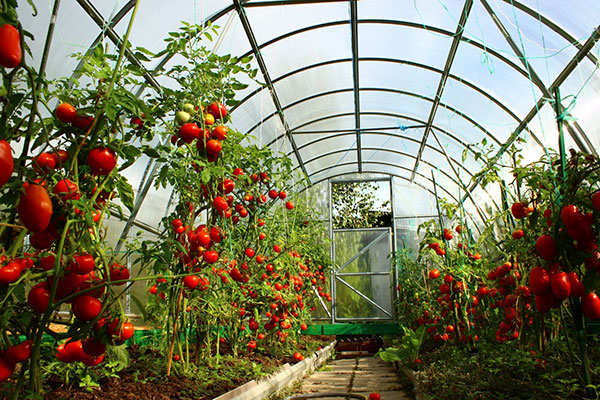  It is also necessary to add slaked lime to this top dressing at the rate of 65 grams per 10 liters of water. After a month, after the first stage of diving of tomato seedlings, a second follows, in which young crops are planted in wide rows. Along the planted tomatoes, it is necessary to provide special grooves, which will then be used for watering.
It is also necessary to add slaked lime to this top dressing at the rate of 65 grams per 10 liters of water. After a month, after the first stage of diving of tomato seedlings, a second follows, in which young crops are planted in wide rows. Along the planted tomatoes, it is necessary to provide special grooves, which will then be used for watering.
It is believed that you do not need to water the tomatoes after sunset, as the soil can cool more at night. Experts advise, instead of outdated irrigation systems using a watering can or a bucket, to use modern - automated, capable not only of controlling the entire process independently, but also turning on and off independently.
Caring for tomatoes during the period of intensive stem growth involves pruning and tying them. This method of growing tomatoes is called trellis.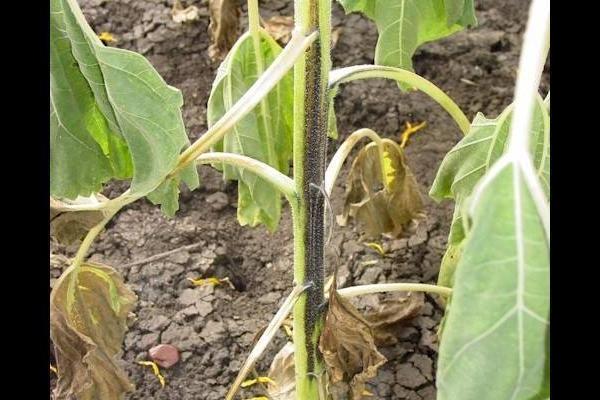  By shaping the bushes in this way, you provide your tomatoes with a good ventilation system and optimal lighting. It is necessary to cut the stems so that no more than three strong shoots remain on the bush after the manipulations. In this case, any intermediate processes should be removed. Tomatoes are tied up so as not to disrupt their normal development.
By shaping the bushes in this way, you provide your tomatoes with a good ventilation system and optimal lighting. It is necessary to cut the stems so that no more than three strong shoots remain on the bush after the manipulations. In this case, any intermediate processes should be removed. Tomatoes are tied up so as not to disrupt their normal development.
Further, caring for tomatoes will require from you only the timely removal of fatty shoots, as well as amendments for the need for garters and supports. In the process of caring for and growing crops, one should not forget about pollination. With the onset of warm days, this function will be gladly taken over by bees, who will be able to enter your greenhouse with the help of a window, coveting a prudently suspended container with jam or sugar syrup.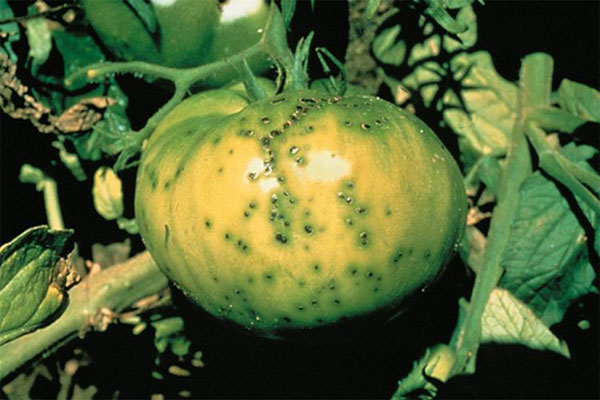
Possible diseases and methods of dealing with them
The main enemies of the tomato growing in greenhouse conditions are viruses, bacteria, fungi and insects. Even with proper cultivation and care of vegetable crops, you can hardly avoid the occurrence of any of the unpleasant diseases. Therefore, it is necessary to have information about all the ailments that tomatoes can overcome, and try to meet them fully armed in order to give a timely rebuff.
One of the diseases is late blight. It is caused by a special microscopic fungus that quickly spreads throughout the plant. Signs of this disease are the presence of a characteristic white bloom on the underside of the leaves, brown spots on them and stems, as well as brown subcutaneous spots.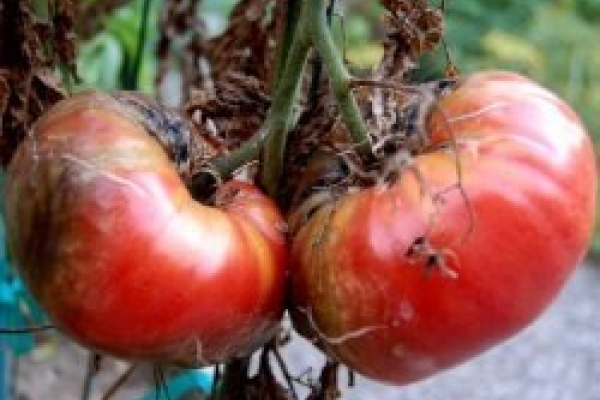  The spread of the disease is facilitated by high humidity and temperature fluctuations. For prophylaxis, three weeks after planting, the seedlings are usually treated with the "Barrier" solution, and after another three - with the "Barrier" preparation. Treatment is carried out with Oxyhom, for which a couple of tablets are diluted in 10 liters of water.
The spread of the disease is facilitated by high humidity and temperature fluctuations. For prophylaxis, three weeks after planting, the seedlings are usually treated with the "Barrier" solution, and after another three - with the "Barrier" preparation. Treatment is carried out with Oxyhom, for which a couple of tablets are diluted in 10 liters of water.
If the green fruits of tomatoes suddenly become watery with a rotten smell or black depressed spots, the plants are affected by apical rot. Its causes can easily be a lack of calcium, excessive nitrogen content in the soil, and insufficient watering of tomatoes. In order to prevent the appearance of this unpleasant phenomenon, proper care when growing vegetables implies sufficient watering of crops, which is especially important on hot days. If the culture is already sick, it must be treated with nitrate solution as soon as possible. To make it, you need to dissolve a tablespoon of calcium nitrate in 10 liters of water. Those fruits that can no longer be cured due to severe disease damage are best burned.
Leaf mold is also a disease quite familiar to many gardeners who decide to grow tomatoes in a polycarbonate greenhouse. Such an ailment is characterized by the presence of brown-brown spots on the leaves, after which the leaves inevitably dry out. Spores of this dangerous fungus can be transferred from crop to crop during the irrigation procedure, and also persist in the soil, on last year's leaves.  Control measures include a decrease in air humidity, a decrease in the number of waterings, and an increase in indoor temperature indicators.For the prevention of the plant, it is recommended to treat it with copper oxychloride at the rate of 40 grams per 10 liters of water, spray it with Oxyhom, Barrier, and Zaslon preparations. It also helps well to disinfect the greenhouse after harvesting vegetables with copper sulfate.
Control measures include a decrease in air humidity, a decrease in the number of waterings, and an increase in indoor temperature indicators.For the prevention of the plant, it is recommended to treat it with copper oxychloride at the rate of 40 grams per 10 liters of water, spray it with Oxyhom, Barrier, and Zaslon preparations. It also helps well to disinfect the greenhouse after harvesting vegetables with copper sulfate.
Another type of trouble is a tomato disease called mosaic. It is caused by special types of viruses and can lead to the death of crops. Its main features can be called shriveled leaves with yellowish-green spots of an atypical shape, the general unsatisfactory condition of the plant, as a result of which both it and the crop perish. To fight the disease, it is customary to remove the affected crops and burn them. Seed treatment with potassium permanganate solution has proven itself well. With the same solution, you need to water the seedlings, taking breaks for about three weeks. Preventive measures include processing the seedlings with skim milk every one and a half weeks. To do this, dilute a liter of milk in 10 liters of water and add one teaspoon of urea.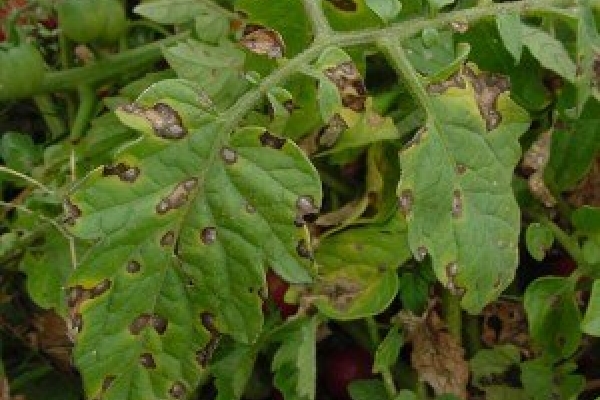  When stepping tomatoes, you do not need to touch the sap of the plants, as the disease can be transmitted through it.
When stepping tomatoes, you do not need to touch the sap of the plants, as the disease can be transmitted through it.
Gray fruit rot can also appear even with proper crop care, as this disease is caused by fungi. Most often it occurs at the end of the growing season, and the signs are small spots that become larger and begin to secrete a brown liquid.
You can also observe the appearance of gray rot, which most often occurs in tomatoes that are grown in polycarbonate greenhouses. To combat this type of ailment, the temperature indicators should be increased, the affected fruits and particles of culture should be removed, and the diseased fruits should be treated with means called Fundazol, "Barrier", "Barrier".
Root rot causes crops to wither as the root of the plant begins to rot. To combat it, it is necessary to treat the soil using a solution of copper sulfate, then remove the affected area of the earth and add a fresh one instead. A good effect is also achieved when processing with the means of "Barrier" and "Zaslon".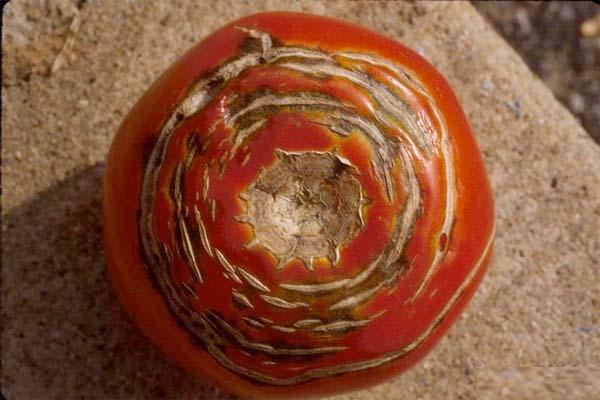
Brown rot or phomosis is spread by fungi. Visually, a brown spot is visible on the fruits, and with the development of the disease, green tomatoes fall off. For prevention, it is necessary to prevent excessive moisture in the soil, disinfect the soil, collect and destroy the affected fruits of vegetables.
Dry spot or macrosporiosis is a disease in which large brown spots are clearly visible on the fruits, and diseased leaves fall off. Black plaque is also characteristic of this ailment. Control measures are similar to those used for late blight.
Fruit cracking is a physiological disease. It can occur when crops are over-watered on dry days. To fight, it is necessary to carry out uniform watering of the soil; on hot days, spray with a solution of lime.
Insects often attack tomatoes.
Medvedka, which digs huge holes and is capable of causing irreparable damage to the crop. To combat it, tinctures of table vinegar and hot pepper are poured into the minks. It is also customary to use the purchased tool "Thunder". Wireworms, caterpillars that destroy stems and roots, also annoy vegetable crops.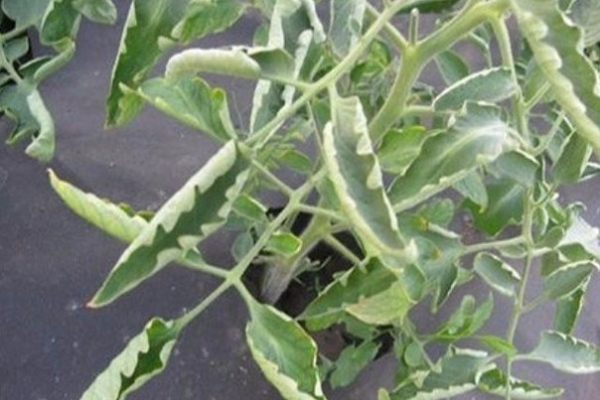  To combat them, vegetables are strung on sticks buried in the ground, on which caterpillars accumulate. When digging up land in a greenhouse, they also need to be collected and disposed of. The introduction of mineral dressings and the addition of lime to the soil will also reduce the number of pests. In greenhouse conditions, tomatoes can also attack whiteflies and scoops. To combat the first type of caterpillars, Citkor and Phosbecid are successfully used.To resist the second, you should promptly destroy the weeds in the greenhouse, dig in the soil well, and carry out the treatment with Strela.
To combat them, vegetables are strung on sticks buried in the ground, on which caterpillars accumulate. When digging up land in a greenhouse, they also need to be collected and disposed of. The introduction of mineral dressings and the addition of lime to the soil will also reduce the number of pests. In greenhouse conditions, tomatoes can also attack whiteflies and scoops. To combat the first type of caterpillars, Citkor and Phosbecid are successfully used.To resist the second, you should promptly destroy the weeds in the greenhouse, dig in the soil well, and carry out the treatment with Strela.
Video "Diseases of tomatoes"
The video is dedicated to such a tomato disease as late blight. Watch the post and learn how to protect tomatoes from this disease.
