How to protect cucumbers in a greenhouse from diseases and pests
Content
The main causes of occurrence
There are a number of reasons why a greenhouse cucumber can become sore. In particular, a violation of the technology of planting vegetables, which includes the use of infected planting material, a sharp change in the microclimate inside the greenhouse, and high humidity. Dangerous and poor ventilation, lack of air exchange, leading to oxygen starvation of plants.
It is important to remove weeds and plant waste from the beds in time, carry out preventive treatment with drugs for diseases and pests, and collect ripe vegetables on time. You can plant a variety of vegetables that are resistant to diseases characteristic of the culture (for example, the Boy with a finger cucumber). Then there is a chance to minimize the risk of trouble.
Video "How to increase the harvest of cucumbers"
In this video, you will learn how to increase the yield and prolong the fruiting of cucumbers.
Common diseases and their treatment
Each of the diseases caused by viruses or fungi have their own symptoms, which make it possible to recognize it and begin treatment.
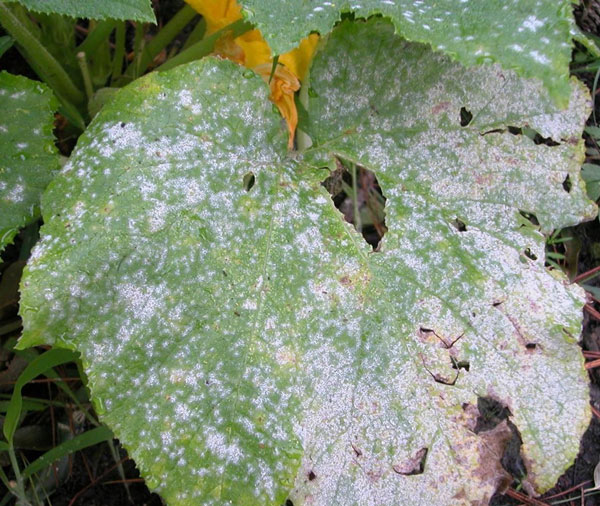
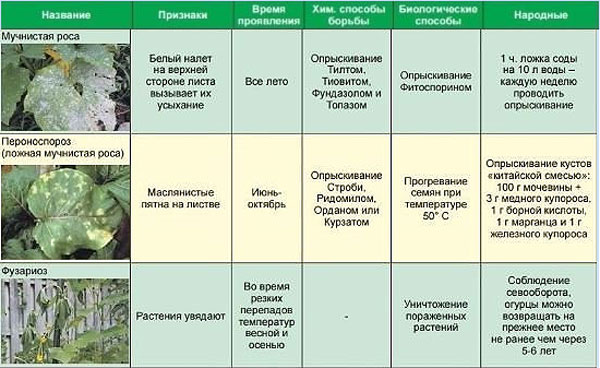
Powdery mildew
This ailment is characterized by the appearance of a white bloom on the surface of the leaf, which leads to drying of the foliage and the death of the crop. Powdery mildew is transferred by weeds, its causative agent is the mycelium of Erysiphales.
There is also downy mildew, or peronosporosis, in the presence of which yellowish-brown spots appear on the foliage, a bloom of a gray-purple hue is visible on the back. The causative agent of the disease is the Plasmopara mushroom.
Both diseases are effectively treated with folk remedies: infusions of mullein and potassium permanganate.
To prepare the first solution, a mullein and 1 spoon of urea are dissolved in 1 bucket of warm water. To obtain a manganese solution, 1.5 g of the product is dissolved in 1 bucket of liquid, then spraying is carried out.
They also use solutions of marigolds and horsetails. Pollination of crops with sulfur placed in gauze also helps. In this case, the greenhouse is preliminarily closed. Of the drugs, Bordeaux liquid, copper and iron vitriol, Topaz, Zaslon, Fitosporin and Fundazol are recommended.
Gray and white rot
Gray rot is caused by the fungus Botrytis cinerea. The foliage and sinuses are covered with grayish spots. The mycelium affects almost all parts of the plant.
White rot or sclerotinia, caused by the same pathogen as gray rot, destroys plant cells, as a result of which they die. The symptom of the disease is a white fluffy and cotton-like plaque.
If the disease is just beginning, spraying with Bordeaux liquid with the addition of copper sulfate and potassium sulfate to the solution will help against gray and white rot. But for the second ailment, dusting of leaves and shoots with copper-chalk powder is additionally used. In severe cases, fungicides are used: "Hom", "Fundazol", "Ordan", etc.
Bacteriosis
The bacteriosis, also known as corner spot, is caused by the pathogen Pseudomonas lachrymans. It can be recognized by light brown spots on the cotyledons. Spotting appears on fruits as well.
If the plants in the greenhouse are affected by bacteriosis, you need to remove the infected parts, treat the bushes with Bordeaux liquid, Fitosporin or Fundazol fungicides.
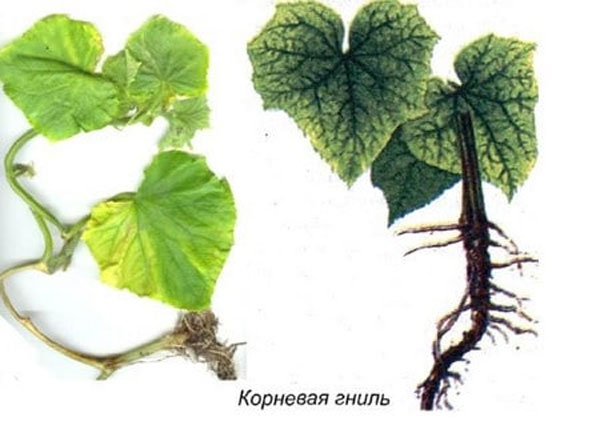
Root rot
The disease manifests itself at the beginning of fruiting, infection can be traced by the stem, which turns yellow and cracks, the leaves of plants wither. Vegetables that have died from rot are best removed from the site and burned.
A solution of copper sulfate effectively helps, for which they take 1 tsp. funds, 3 tsp. wood ash per 0.5 liters of water. Crushed coal, chalk or ash is applied to the affected parts of the culture, after which they need to be dried. Biologics "Baktofit", "Pseudobacterin-2" and "Trichodermin" are used.
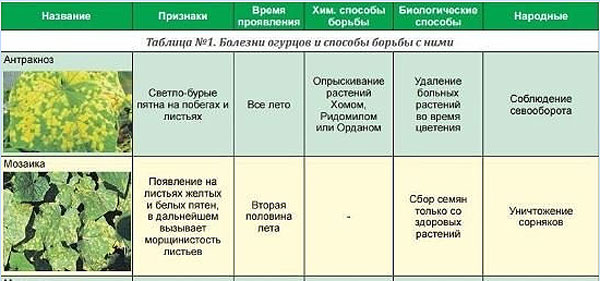
Anthracnose
Fungal disease affecting the entire plant. Yellowish spots can be seen on the surface of leaves and stems. The affected parts crumble and die off, the fruits do not last long and acquire a bitter taste.
To help the plants, they are sprayed every day with a Bordeaux mixture, and a suspension of bleach is also used - 40 g of funds per bucket of water, which must be treated with crops once every 10 days.
How to deal with pests
Among the pests of cucumbers growing in the greenhouse, the most common are spider mites, melon aphids and greenhouse whiteflies.
Spider mite
This pest feeds on both seedlings and adult bushes. You can recognize the presence of parasites by the characteristic cobweb that covers the plants, along which ticks move.
Acaricidal agents are used to kill insects. It is advised to process crops with Akarin, Bicol, Fitoverm and other preparations. Of the folk methods at the initial stages of planting infection, a solution of onion is effective. For cooking, take 1 spoonful of chopped vegetable, add a spoonful of pepper, liquid soap and wood ash. Shoots are sprayed once every 5 days. The tincture of bitter pepper is used in a similar way.
Melon aphid
Aphid colonies parasitize greenhouse plants, sucking juice from green parts. At the initial stage of infection, wrinkling of leaves and stems is observed.
To destroy melon aphids, an infusion of red pepper and tobacco dust is used: 30 g and 200 g, respectively, for 10 liters of hot water. Having insisted for a day, 1 tbsp is added there. l. liquid soap and 3 tbsp. l. wood resin. Of the purchased drugs, Inta-Vir and Strela are helping.
Greenhouse whitefly
Such insects feed on plant sap, after which sugary secretions appear on the surface, on which fungi parasitize. Over time, if you do not take action, cultures wither and die.
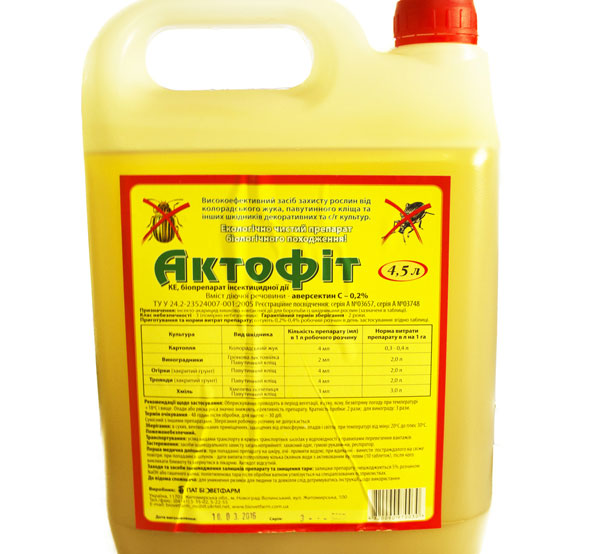
Landings should be treated with pork, sheep, horse, cow, rabbit humus. Spraying with the biological product "Aktofit" 2-3 times during the entire growing season will also help.
Prevention measures
Protection of greenhouse plantings implies constant cleaning of rotten fruits, affected and dry parts of plants, disinfection of the greenhouse, soil and equipment. Among the preventive measures, one should mention the maintenance of the temperature regime at the level of + 23 ... + 25 ° C, air humidity - at least 80%. Sowing of varieties resistant to diseases, warming up and dressing of planting material is carried out.
It is important to observe crop rotation, constantly ventilate the greenhouse and properly care for the plants.
Knowing the causes and symptoms of diseases will help every gardener to detect the disease in time and save his harvest.