27 of the best zucchini zucchini varieties and outdoor cultivation features
Content
- 1 Description
- 2 Video "Differences between zucchini and zucchini"
- 3 Growing
- 4 Varieties and hybrids
- 4.1 Aeronaut
- 4.2 Banana
- 4.3 White
- 4.4 Waterfall
- 4.5 Gribovsky
- 4.6 Diamond
- 4.7 Yellow-fruited
- 4.8 zebra
- 4.9 Zolotinka
- 4.10 Iskander
- 4.11 Kavili
- 4.12 Lagenaria
- 4.13 Jellyfish
- 4.14 Ball
- 4.15 Negro
- 4.16 Nephritis
- 4.17 Odessa
- 4.18 Parthenon
- 4.19 Ronda
- 4.20 Skvorushka
- 4.21 Sosnovsky
- 4.22 Spaghetti
- 4.23 Tiger cub
- 4.24 Pharaoh
- 4.25 Tsukesha
- 4.26 Black handsome
- 4.27 Anchor
Description
Zucchini differs from zucchini not only in appearance, but also in terms of ripening, taste and structure.
How is it different from a vegetable marrow?
It is difficult to confuse zucchini with zucchini, because even outwardly they are different. The main feature is the skin color of vegetables. In zucchini, it is white, with a shade of green, while in zucchini it is deep green. Hybrid varieties of a vegetable that has recently appeared in our country have a rich color range.
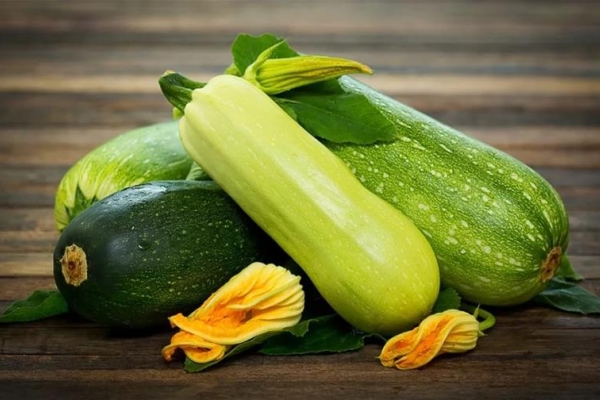

The zucchini has a light skin color, the zucchini has a dark color
The second difference is the size of the fruit. Zucchini, familiar to us, grows to unpredictable sizes, and other ovaries on the bush disappear. Zucchini is much smaller in size - its length does not exceed 30 cm.
The ripening period is considered the advantage of zucchini. The fruits become ripe after a week, the harvest is harvested from the zucchini much later.
The seeds of these vegetables also look different. In a vegetable marrow, you can immediately see them, because the size of the seeds cannot be called miniature. Zucchini fruits have such small seeds that they are difficult to see.
In terms of taste, zucchini surpasses a traditional vegetable, because its flesh is very tender, with light sweetish notes.
Calorie content and nutritional value
Zucchini has 27 kcal, zucchini - 16 kcal. That is why vegetables are the main ingredient in many dietary meals. In addition, they are easily absorbed in the body, so the fruits are often used for the first feeding of children.
The composition of zucchini is rich in nutrients and minerals. The main elements are magnesium, potassium and phosphorus. In addition, the composition contains:
- iron;
- sodium;
- calcium;
- zinc;
- thiamine.

Table: chemical composition of zucchini
Benefit and harm
The rich composition of the vegetable determines its active use in health and healing diets, as well as for the prevention of many diseases and strengthening the body:
- activation of digestive processes;
- improving intestinal motility;
- removing excess fluid from the body;
- improving the condition of the skin, nails, hair, teeth;
- relief of the course of gout, inflammation of the kidneys, metabolic abnormalities.
The beneficial properties of the fruit are associated with the high content of vitamin C, folic acid, carotene.
However, the vegetable also has a contraindication. The main thing is associated with the presence of oxalate in the composition. Therefore, people suffering from diseases of the gallbladder, urolithiasis or malfunctions in the processes of removing calcium from the body should stop using zucchini.
Video "Differences between zucchini and zucchini"
This video highlights the differences between two vegetable crops.
Growing
Gardeners who decide to plant zucchini on their plot should know about two methods of growing a crop - seed and seedling. In addition, it should be understood that this plant is more demanding to care for than regular squash. What should be the ideal conditions?
Soil preparation
When preparing the soil, you need to keep in mind some recommendations:
- It is better to dig up the ground in the fall. It is recommended to feed the soil with rotted manure or chemical compounds such as superphosphate. If the soil is too acidic, wood ash is added to it.
- The best predecessors for zucchini are legumes and nightshades. On the other hand, pumpkin crops will have an adverse effect on future planting.
- Before spring planting, the site should be re-dug up. You can add an additional dose of fertilizer and, if necessary, disinfect the soil.
Germinating seeds
Pre-soak the seeds. To do this, they are placed in a damp cloth, which is constantly sprayed as it dries. When the seeds "hatch", they are sown in a special container or peat pots.
Planting seeds consists of the following steps:
- Soil preparation. To prepare a nutrient substrate, the soil is mixed with compost and wood ash.
- Formation of holes. Given the fact that culture loves space, the holes should be made at intervals of 20 cm.
- After planting, the soil must be leveled slightly.
Planting seedlings
Before planting, the zucchini seedlings are hardened. To do this, the seedlings are taken out into the fresh air for several hours, and brought back into the room at night.
The best place in the summer cottage will be sunny areas, protected from through winds. The main issue in the process of planting seedlings is soil preparation. It is pre-dug up, fertilized and loosened.
If clay soils are used for planting, then sand and compost must be added to them, if sandy - sawdust. Organic fertilizer is poured into holes prepared in the open field. For planting seedlings, it is recommended to choose non-sunny weather or evening time of the day.
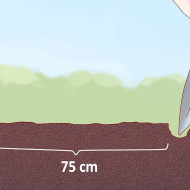
The holes should be made at a distance of 80 cm from each other.
- Hole preparation
- Planting seedlings
- Dive seedlings
Watering
Moistening the soil must be carried out regularly and in moderation. Excessive watering will inevitably lead to the development of fungal diseases, and a lack of moisture will destroy the plant. In irrigation, the most important issue is the water temperature. It should be 20-23 ° C. It is undesirable to neglect this requirement, since watering with cold water significantly increases the risk of root rot.
Top dressing
Zucchini does not need constant feeding, however, the flowering period presupposes fertilization of the soil. The best option, according to gardeners, are complex mineral fertilizers. In addition, organic fertilizing is actively used.
Harvesting and storage
Zucchini fruits are stored much longer than a white-fruited zucchini. Harvested about 2-3 times a week, after which the fruits are consumed fresh or sent for conservation. To collect the seeds, the zucchini is stored in a bright, cool place.

Zucchini fruits are stored much longer than a white-fruited zucchini
Diseases and pests
The culture is generally resistant to many diseases. But sometimes the plant is affected by such diseases:
- anthracnose;
- ascochitis;
- bacteriosis;
- apical bacteriosis;
- dry top rot;
- fusarium;
- powdery mildew;
- downy mildew;
- white rot;
- gray rot.
The most dangerous pests of the pumpkin crop are called spider mites, whiteflies and melons aphids. To protect your plantings from the attack of pests, you need to organize the correct watering and feeding regime, and carry out preventive treatments.
Varieties and hybrids
Numerous varieties and hybrids bred during breeding allow every gardener to choose a zucchini that will feel comfortable in domestic beds.
Aeronaut
One of the best early maturing varieties, grown in open and closed ground. Fruits are dark green with many small dots.
Banana
A hybrid variety whose fruit really looks like a banana. Zucchini tolerate transportation well, can be stored for a long time without loss of taste.

A characteristic feature of the Banana variety is a rich yellow hue of the peel
White
The fruits are characterized by a milky hue and thin skin. The culture is unpretentious in care, it endures temperature extremes and frosts.
Waterfall
The variety is hybrid. Has early maturation and high rates of disease resistance. Produces, as a rule, a bountiful harvest. Fruits reach 600 g.
Gribovsky
The fruits are white in color and grow up to 30 cm in length. The cultivar matures about 50 days after planting. During the growing season, forms long branches.
Diamond
The variety was bred by German breeders. Begins to bear fruit 40 days after planting in the ground, therefore it is considered the earliest.
Yellow-fruited
The fruits are characterized by a yellow color and delicate flesh. The crop is resistant to pests and easily tolerates transportation.
zebra
By description, it is similar to yellow-fruited zucchini. Possesses high rates of fruiting. A special feature is the unusual color of the fruit - dark green with white stripes.
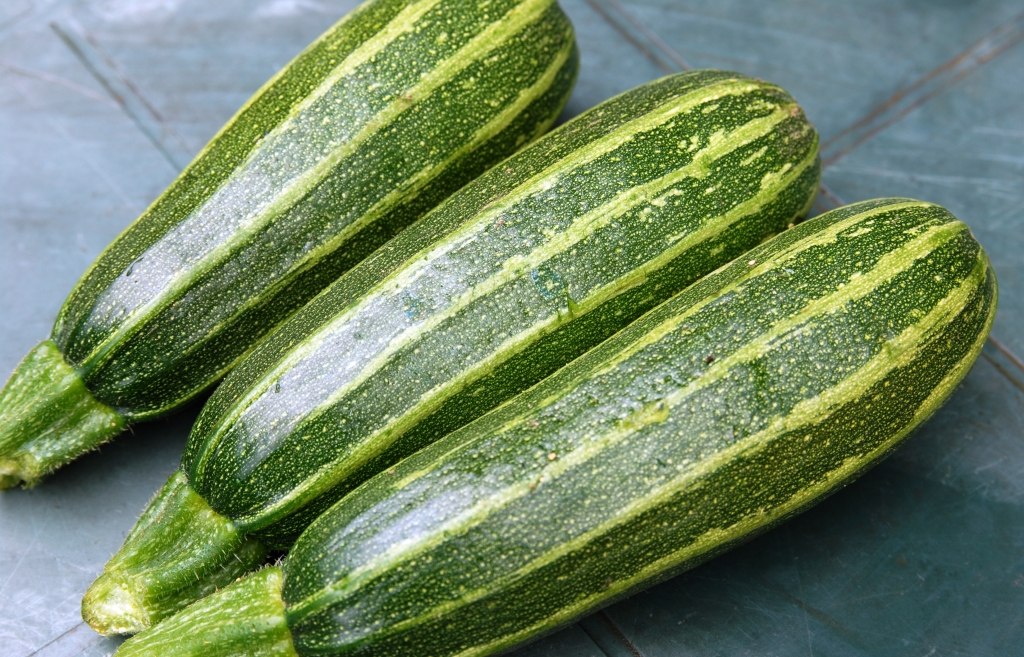

Zebra variety attracts attention with striped color
Zolotinka
The crop can be harvested 43 days after the first shoots appear. The plant has a branched structure, therefore, requires a sufficient amount of free space.
The fruits of Zolotinka are bright yellow in color and have excellent taste.
Iskander
A hybrid variety created by breeders from Holland. Vegetables have a light green hue, thin peel and soft pulp. The culture ripens 45 days after germination.
Kavili
An early ripe hybrid with high fruiting rates. Vegetables grow up to 25 cm in length and have a greenish tint.
Lagenaria
Another name is Calabaza. The most unusual variety, due to the original shape of the fruit: elongated, reminiscent of a ram's horn. The variety has a long ripening period.
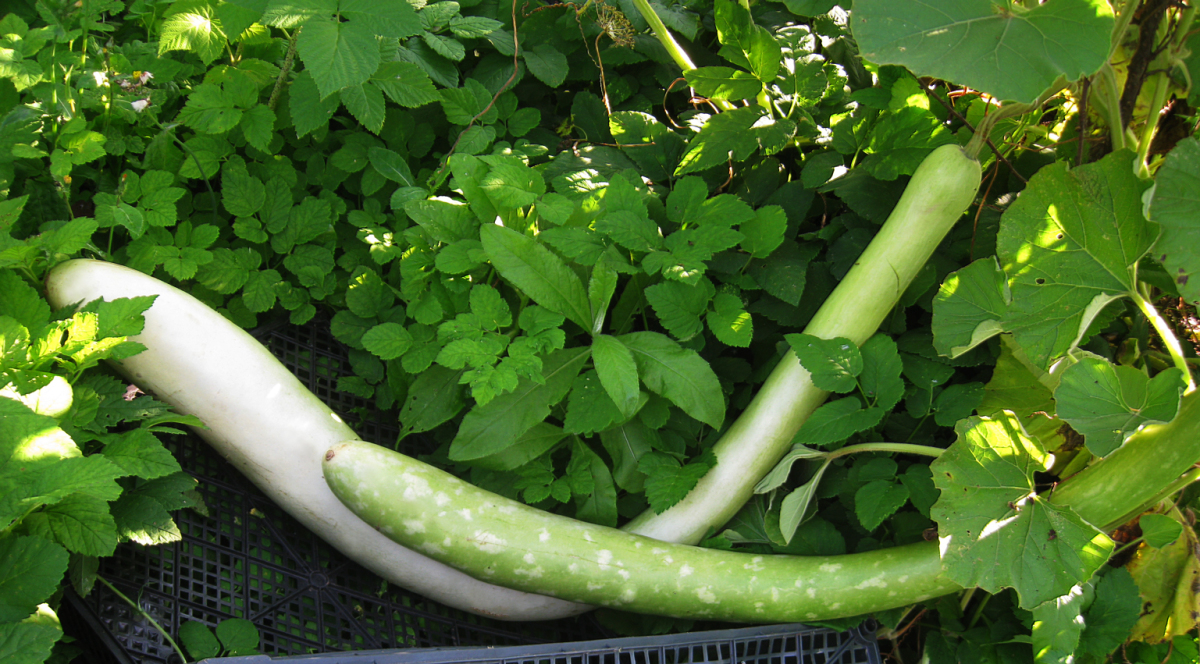

The fruits of the Lagenaria variety have a curved shape.
Jellyfish
It matures for about 37 days. Resistant to temperature fluctuations, frost and drafts. The mass of ripe fruits can reach 1 kg.
Ball
The variety is characterized by ball-shaped fruits. Color - dark green speckled. Ripening period is about 60 days.
Negro
The variety is characterized by compactness, small leaves. The vegetables have a cylinder-like shape, delicate flesh and thin skin. The culture easily adapts to almost any climatic conditions and resists disease well.
Nephritis
As a rule, up to 30 fruits ripen on one shrub, therefore this variety is considered the most productive. The fruits are dark green, with a dense skin and juicy pulp.
Odessa
This variety is resistant to many fungal diseases. Fruits are medium in size, are actively used in conservation and are suitable for fresh consumption.
Parthenon
The variety is bred by Dutch breeders. The fruits have a glossy thin skin. The variety bears fruit even in unfavorable conditions.
Ronda
The variety has a long ripening period, but the fruiting rate is high. The vegetables are characterized by an unusual spherical shape and green color. Zucchini is often used in home preservation.
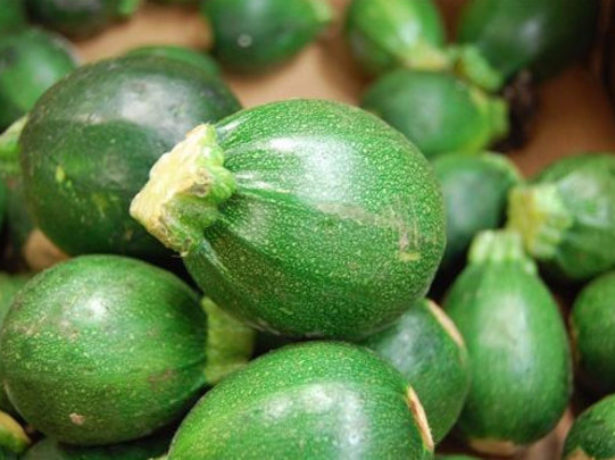

The Ronde variety is characterized by its spherical shape and green color.
Skvorushka
The variety bears fruit well, is resistant to fungal diseases and frost. The fruits are in the shape of a cylinder with a characteristic barely noticeable ribbing. The taste of zucchini is delicate, sweetish.
Sosnovsky
The variety bears fruit with milky and creamy zucchini.A characteristic feature is considered to be good resistance to pests and adverse weather conditions.
Spaghetti
A characteristic feature of the Spaghetti variety is the ability of the pulp to exfoliate into fibers, forming a kind of "spaghetti". The culture has a late ripening period, so it can be successfully grown in regions with a full and long summer.
Tiger cub
The fruiting period reaches 70 days. Ripe vegetables have an elongated shape and a characteristic dark green color. The variety easily tolerates prolonged water shortages.
Pharaoh
A characteristic feature of this variety is the ability of the fruit to change its color depending on the degree of ripeness.
The unripe fruits of the Pharaoh, as a rule, are colored greenish, and ripe ones - black.
Tsukesha
This is perhaps the most versatile variety. It can be grown in all regions of Russia, as it quickly adapts to any weather conditions. Tsukeshi fruits are often added to salads.
Black handsome
Vegetables are dark, close to black in color. The culture is resistant to disease and can be easily transported.
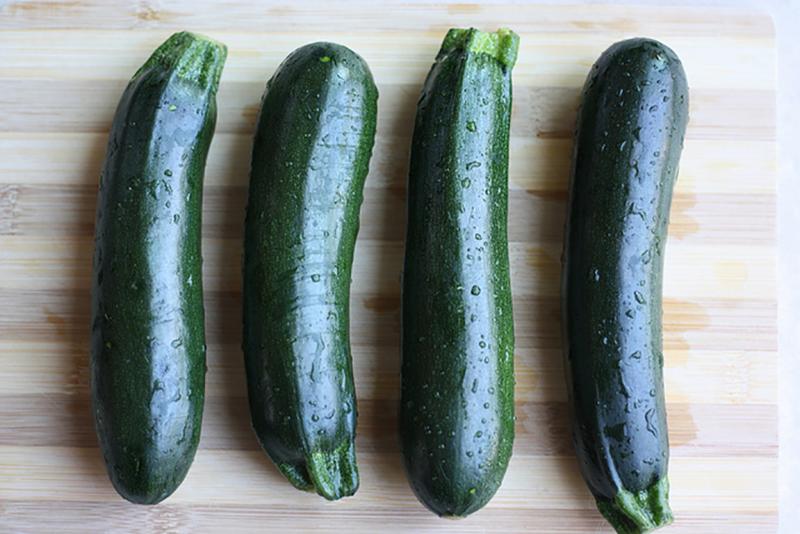

Zucchini Black handsome has a dark skin tone
Anchor
A characteristic feature of the variety is considered to be a long fruiting period - until the arrival of the first frosts. The anchor is resistant to water shortages and produces a bountiful harvest.
Zucchini belongs to the category of pumpkin crops that are relatively unpretentious to grow. Compliance with the elementary conditions for keeping the plant will provide the gardener with a good harvest of healthy vegetables.