How and what to treat melon from diseases and pests
Content
Diseases and pests
Low temperatures, high humidity, lack of heat and sun - all these factors contribute to the development of putrefactive processes on leaves and fruits. Most often, melons are prone to diseases caused by a fungal infection that affects plants if not properly cared for.
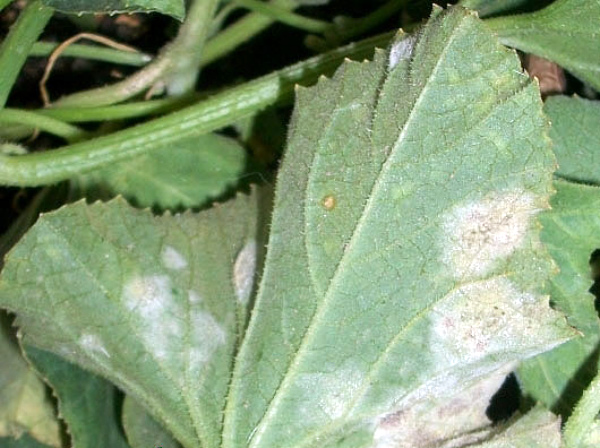
Powdery mildew. At the initial stage, it appears as whitish spots on the greenery of plants (leaves, stems). If measures are not taken in time, the spots become brown and spread over the entire surface, and the leaves themselves dry out. This process leads to a halt in the growth of fruits and a decrease in their quality. In many cases, the disease affects not only the greens, but also the fruits themselves.
Fusarium. This is a fungal disease that manifests itself in the wilting of the leaves. As a rule, it occurs during the formation of the first leaves, active growth and ripening of fruits. In the absence of immediate measures, wilted leaves, and then the stems, lose their color, become covered with spots. It is no longer necessary to count on a generous harvest, since the process is developing so rapidly that literally in 7-10 days the infected plant dies. If the fungus hit the melons at the stage of fruit ripening, then the melons will not be sweet and aromatic enough. It has been noticed that the disease more often affects varieties of melons of the middle and late ripening period.
Copperhead (anthracnose). Signs are brown spots on the leaves, gradually increasing in size. Over time, holes form in the affected areas, the leaves dry out and curl around the edges, the stems become brittle, and the fruits become deformed, begin to taste bitter and gradually rot.
Root rot. Young weakened plants are more susceptible to the disease. At the initial stage, it is manifested by drilling and thinning of the stem, gradually leading to the death of cotyledons, leaves and roots.
In addition to various kinds of diseases, planting melons is often also attacked by insect pests, which we will talk about later.
Melon fly. In some regions, this pest is the main enemy of melons, as it affects up to 50% of the total crop. It is quite difficult to get rid of flies, since they easily tolerate the cold, and winter safely in the ground in the form of larvae. These insects begin their years around the beginning of June and can even penetrate the ovary. Basically, the pest attacks already ripe fruits. In this case, the insect pierces the soft tissues of the fruit and lays several larvae inside the melon.
The first signs of fruit fly infestation are small bumps on the skin where the pest enters. Then, when the eggs of the insect turn into larvae, holes (soft passages) can be seen on the surface of the melon, which these same larvae pierced. Fruits, after being damaged by a pest, begin to rot quickly, and the risk of their infection with fungal diseases also increases. Of course, eating a melon infested with insects is not recommended, even if the flesh of the fruit is not yet severely damaged and the larvae are easily removed.
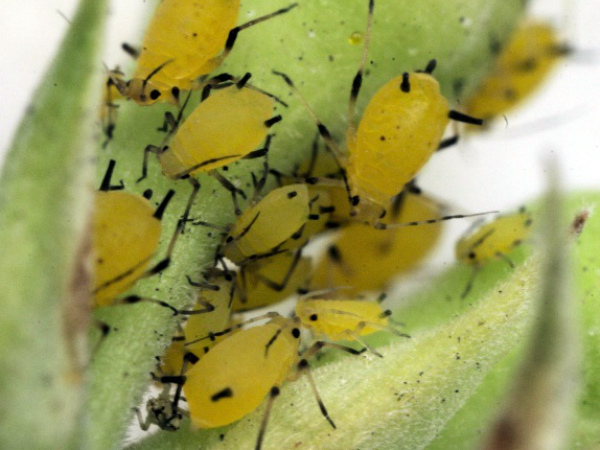
Melon aphid.Represents multiple clusters of small insects below the leaves. Arranging in groups and laying the larvae there, they suck the juice from the leaves, which leads to their yellowing, twisting and wilting. In this case, the whole plant suffers, and the flowers and ovaries fall off.
Wireworms. These are the larvae of beetles, which are popularly called click beetles. Their body really looks like a piece of wire, it is very strong and springy. The larvae live in the soil, feeding on the seeds of melons, so the main harm is done to the rhizomes of the melon. They gnaw through the roots and the underground part of the stem, which leads to a delay in development, and then to the death of a young plant.
Spider mite. These pests settle on the lower part of the leaf. Tick infestation is evidenced by thin cobwebs that twine around the leaves. During the day, adult beetles lead a hidden life, hiding in the cobweb and laying larvae there. Colonies feed on plant sap, so small spots can be found on the leaves - traces of pest bites. Infected leaves turn yellow, deform and fall off, after which insects move to stems, flowers and ovaries. Devouring them, they gradually destroy plants.
Gnawing scoops. These are caterpillars that live both in the soil and on its surface. In the daytime, they prefer to hide from the sun in the ground, where they gnaw at the roots of plants, and at night they climb to the surface and damage the stems there. Massive damage leads to the death of melons, especially if the root is damaged.
Video "Protection of melon flies from melon flies"
From the video, you will learn how to protect your garden and melons from one of the most dangerous quarantine pests of melon, watermelon, pumpkin and cucumber, which causes great harm to the crop.
Processing tools
Many diseases can be avoided if you adhere to the rules of agricultural technology for a given crop:
- do not plant in heavy and too moist soil, as this contributes to the development of fungal diseases, putrefactive processes and fading melon planting;
- observe crop rotation - it is not advisable to plant melons after nightshade crops (potatoes, tomatoes, eggplant), in addition, the place for a garden with melons must be changed annually;
- plants that have been exposed to diseases or pests must be burned, after which a deep digging of the soil must be carried out;
- and the main measure in the fight against pests and diseases is seed dressing in disinfecting solutions (manganese, copper sulfate, "Formalin", "Fundazol" and other similar means).
These simple agronomic measures will reduce your melons' risk of diseases such as fusarium, root rot, and many other fungal diseases. If, nevertheless, the plants are sick for some reason, then the only way to solve the problem will be fungicides, since folk remedies are effective only at the initial stage of the disease.
To combat powdery mildew, colloidal sulfur is used - it is a white powder to protect vegetable and fruit crops from the above diseases. The drug is used as a solution (0.3%) or as a plant pollination agent. The effect is observed after 1 day. If the lesions are extensive, the treatment is carried out 1 time / 1 week until all signs of the disease disappear.
Of the folk remedies for this problem, infusion of hay dust or liquid manure is effective. A product is being prepared at the rate of 1 part of organic matter to 3 parts of water. Manure or dust is poured with water and insisted for three days. After that, filter, dilute with water in a ratio of 1: 3, add copper sulfate (5 g / 1 bucket of liquid), and spray the plants. A more gentle remedy is milk or whey diluted 1:10 with water.
For the prevention of powdery mildew, it is recommended to spray melon with Bordeaux liquid 1 time / 7–8 days. For fusarium, a solution of potassium chloride is used, which is watered over the beds during the period of bud formation.To prevent anthracnose, melons are sprayed with a solution or sprinkled with dry sulfur powder 1 time / 10-12 days.
Melon pests need to be treated repeatedly. For example, the melon fly is active during the growing season of plants and during the ripening of fruits, so 2-3 treatments must be carried out per season. The drug "Kemifos" (insecticide) is effective. It is used for spraying at the rate of 10 ml / 10 l of water. For prevention, melon is sprayed with Rapira solution.
For aphids, solutions of Karbofos (10%), Aktelika (30%), or soap solution (100 g soap / 10 l of water) are used. The preparations "Fitoverm" or "BI-58" will help get rid of spider mites. These are universal insecticides used to treat fruit and vegetable crops. Gnawing scoops are destroyed by the preparations "Volaton", "Decis". These are chemicals that are diluted in accordance with the instructions.
It must be remembered that eating a melon treated with insecticides is allowed no earlier than a month after the last treatment.
Processing technology
The treatment of melons from pests and diseases can be carried out in several ways: by spraying the tops, sprinkling the leaves (dry powders are used), or by watering.
Whichever method you choose, to achieve the desired effect, you must adhere to the following rules:
- It is better to spray the plants in cloudy and calm weather (late in the evening), since the strong sun can lead to burns of the treated leaves, and the wind can partially blow off the drug, which will lead to a decrease in its effectiveness.
- The processing time must be calculated so that at least 6-8 hours after the procedure there is no rain.
- Try to spray only plants, avoiding the ingress of drugs into the soil, or, conversely, if necessary, water the soil without getting on the leaves.
- It is not recommended to process the fruits themselves, since insecticides and fungicides tend to accumulate, and these are strong chemicals.
It is also important to adhere to the rules for working with such drugs. When processing melons, be sure to use rubber gloves, a mask and protective clothing, since these agents quickly penetrate the respiratory tract and are absorbed into the bloodstream, which can lead to poisoning. Use a quality pneumatic spray gun for the job.
Remember that the working solution can be stored for no more than a day.
Video "How to increase the yield of melons"
In this video, you will learn how to care for melons to boost yields.