Winter grafting-growing seedlings
The connection of two parts of plants in such a way that together they successfully continue to grow and give tangible progress in development and fruiting is called grafting. It allows you to grow seedlings faster and harvest richer crops. Often, gardeners plant seedlings with the onset of positive temperatures, that is, in spring. However, in recent years, numerous studies and experiments show that winter grafting of apple trees and fruit crops gives high positive results, it is currently more technological and promising.
Content
Training
In winter, seedlings are grafted from early January to early spring, but no later than two to three weeks before planting. Finding the right stock is a paramount and important task, since not all of them can provide fruits of the required quality. The scion and rootstock are harvested in the fall. They are stored in a cool basement in wet sand. It is not recommended to keep them buried in snow, since the weather in winter is very unstable - frequent thaws are replaced by a sharp cold snap, which can cause the death of buds and wood or freezing of the rootstock roots.
Before the soil freezes, the required number of first-class two-year rootstocks with a developed root system is dug. In this case, the diameter of the stem of the root collar should be at least 8 mm. The above-ground part of the rootstock is shortened to 25-35 cm. If a suitable rootstock is not available, root pruning can be used, the length of which should be at least 20 cm and the thickness of 1-2 cm.
The harvested material is tied into bundles, the upper end is marked at the root segments, this will avoid mistakes during grafting.
Scion cuttings are also harvested in the autumn, before the onset of cold weather. A few weeks before grafting, it is advisable to transfer the rootstocks to a room with a temperature of 15-17 C and re-lay them with moist moss, sand or sawdust. After that, thoroughly wash the root system, discard the slightly frozen and diseased cuttings. Selected healthy cuttings are placed in water for a day.
Grafts are brought into a warm room a day or two before grafting and also kept in water. Before the grafting itself, the sorted cuttings are placed on the work surface and covered with a damp cloth.
Vaccination technique
There are several ways to get vaccinated: single or double, copulation, according to the Khudyakov method, in a butt with a tongue or with a saddle-type shoulder. In practice, a method is chosen based on the quality of the stock material and the direction of work.
In general, there are two main methods in the technology of plant grafting - copulation and budding. The first consists in grafting with a cuttings, which already have two or more buds, the second - in grafting with a part of the bark, which contains only one bud.
The grafting technology includes a relatively simple but time-consuming chain of operations: selection of a rootstock-scion combination, preparation of rootstocks, direct grafting, growing seedlings.
Where do you start?
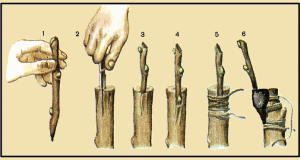
In the designated place, an oblique even cut is made using a copulating knife, about 2-3 cm long.At a distance of about 1/3 from the upper end of the cut, a cut is made deep into the wood for the entire width of the grafting knife, so an oblique cut with a tongue will appear on the stock.
A similar cut is performed on the lower part of the scion branch, the only difference is that the incision is made, retreating one third from the lower edge of the oblique cut. After that, 2-5 buds are counted on the branch from the lower end, and a slightly beveled cut is made above the upper end. Then the components are connected, making sure that the tongue on the handle fits into the gap on the rootstock cut. It is desirable that the cuts on the rootstock and cuttings are the same, then the coincidence of the cambium layers is ensured. In the case when the thickness of the stock is slightly greater than the thickness of the cutting, the grafted components are aligned on one side, and the other side is cut along the border of the cutting.
The junction of the components is tied with a tape of dense plastic film from the bottom up and tied very tightly. After that, the upper cut of the cutting must be covered with a thin layer of garden varnish. The roots of the stock are cut to 18-20 cm so that they do not bend during planting. Then, for a few seconds, the graft cuttings are dipped into a container with paraffin, heated to 62-65 C, making sure that the very site of inoculation does not get into the paraffin.
Storage
Next, the grafted plant is placed horizontally in a box, the walls and bottom of which must be covered with a polyethylene film with small cuts, and sprinkled with steamed and treated with potassium permanganate sawdust. It is advisable to move the box to a warmer room. Often, the fusion of components lasts about 12-14 days for pome crops and 8-9 days for stone fruits. A good adhesion at the fusion point indicates the end of this process.
Already grafted seedlings are stored at a rather low temperature in a basement or a snowdrift before they are directly planted in open ground. They are planted with the onset of a stable warm temperature.
When planting, they are buried to a place tied with a film, and spud up to the level of the upper bud of the scion. Water abundantly, and young shoots are immediately cut off. You can get acquainted with the technological process of winter grafting of cuttings in the video below.
Young shoots soon begin to grow from the buds of the scion. When they reach about 10-15 cm, they leave the dominant one, and the rest are carefully removed. At least 2 months after planting, the harnesses can be removed from the vaccination site.
Annuals grown from rootstocks grafted in winter grow much weaker in most areas of the country than the same seedlings after spring budding. Therefore, it makes sense to leave such seedlings for growing for another year. High positive results are obtained by planting in greenhouses from a dense film according to the 45 x 15 cm scheme, several weeks earlier than usual. In such conditions, the growth rate of plants increases by 2-2.5 times.
However, in cases where it is not possible to use greenhouses, seedlings of fruit crops can be grown on a windowsill in a city apartment. After treatment with hot paraffin, the plants are planted in bags of dense polyethylene with dimensions of 18 x 35 cm, in the bottom of which holes must be made for ventilation.

In order to ensure the vascular connection between the stock and the scion as soon as possible, the plant must be kept in a warm and constantly moist soil, preventing it from drying out. This process of fusion between the root and the cutting is called stratification. It can be achieved by maintaining optimal conditions for the development of root pressure, which is necessary for the formation of callus and its speedy transformation into vascular tissue. The chances of survival will be maximum if the root pressure of the scion is sufficient, a water film will be constantly present on the graft and there will be no premature bud germination.
Winter grafting makes it possible to evenly distribute the load over the seasons. In addition, it can be carried out throughout the winter in comfortable conditions for the gardener - at the table and in the warmth, which is the best option for people with back pain. In addition, its process is mechanized.A clear advantage of the winter scion is the ability to produce seedlings with a closed root system, and they have clear advantages over seedlings with bare roots. And also an important factor is that this technology can significantly speed up the process of obtaining marketable seedlings, on average by 1.5-2.5 years. Step-by-step instructions for winter vaccination are covered in the attached video.
Video "Winter grafting of an apple tree"
The video will tell you about the techniques and principles of effective grafting of fruit crops (stone fruit)
