Fruit rot of apple trees (moniliosis) - methods of struggle
Many people, whether they are gardeners or lovers of country holidays, have seen rot on an apple tree or its fruits more than once. This disease is called fruit rot of apple trees, which is considered the most common disease of this fruit tree. Another name for this disease is apple moniliosis. In terms of its harmfulness, it even surpasses scab.
Content
What is it?
Fruit rot or moniliosis is a fungal disease that can infect a wide range of plants. The causative agent of this disease is the ascomycete mushroom Monilinia cinerea Honey, which belongs to marsupials. Fighting it is an important part of caring for apple trees.
This disease is characterized by two stages:
- conidial stage. It is caused by the fungus Monilia cinerea Bon. In this case, the formation of sporulation occurs in all affected areas of the tree, which looks like small and gray pads. These pads are composed of unicellular chains of colorless conidia. In the spring, conidia infect flowers and, spreading along the shoot, provoke the development of a monilial burn. During the growing season, the fungus produces several generations of conidia, leading to massive infestation of the entire tree;
- sclerocial stage. This is the so-called resting stage.
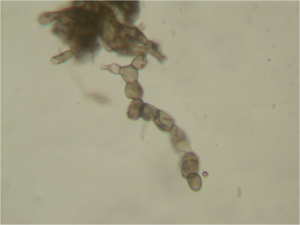
Some scientific articles distinguish two forms of this disease:
- fruit rot - the primary lesions are localized on the fruits, which leads to their rapid deterioration and unsuitability for human consumption. Develops throughout the entire fruiting period;
- monilial burn or leaf burn - the disease affects flowers, ovaries, branches and leaves, leading to their drilling and drying. Being on a tree for a long time, they acquire a burnt appearance.
The greatest danger to the apple tree is infection of the bark of the branches, which leads to the development of cracks and wounds on it, from which an abundant release of gum occurs. This gray mold can dry out large areas of wood as well as overgrown branches. In the most severe cases, the lesions affect the entire tree. The fungus hibernates mainly in the form of mycelium on fruits (fallen or left hanging on the branches) and branches. For certain regions (Moldova, Caucasus, Crimea), it can also winter in the form of conidia. With the onset of spring, conidial pads are formed in the infected areas, which leads to a spring exacerbation of the disease. The mushroom carries out the full cycle of its development during the fertile period.
Causes of occurrence
There are many factors that contribute to tree infection. However, the main reason that leads to the development of fruit rot is the infection of the apple tree with actinomycetes.
The main reasons include:
- various damages in the bark (especially cracks);
- contact of mummified infected fruits with healthy parts of the apple tree;
- damage to the skin of apples due to insect bites (mainly goose and moth);
- the presence of other diseases affecting apple trees;
- the presence of phytopathologies;
- contact of various parts of the tree with already infected fruits (especially those already mummified) or branches;
- high susceptibility of a certain apple variety to this disease. But often even varieties that are resistant to this disease are powerless to resist it;
- not destroying infected apples and branches that may accumulate under the tree, thereby contributing to further infection.
Factors that create suitable conditions for infection:
- flowering period;
- past hail;
- infection is possible through the petiole fossa, but subject to the presence of droplet-liquid moisture in it;
- air temperature about +15 degrees;
- high air humidity (70% and more);
- dirty containers that were used to collect apples;
- dirty tools used for pruning or grafting;
- non-disinfected premises that were used to store garden tools;
- windy weather (in this way the spores of the fungus spread);
- heavy precipitation (fog, snow, rain);
- winter with abundant snow cover;
- cold lingering spring.
Symptoms
An incubation period is characteristic of fruit rot. It takes about five days from the moment of infection to the appearance of the first symptoms, and sporulation begins after 10 days. Actually, after this, the tree begins to hurt.
Fruit rot symptoms:
- first, the formation of the first wormy carrion occurs (in summer varieties earlier, in winter varieties later);
- the fruit pulp becomes soft and brown;
- the apple starts to rot from a small brown spot;
- this spot gradually increases in size;
- it covers most of the fruit;
- pads form in large numbers on the surface of a rotting apple;
- the pads are gray and may turn white against the brown apple;
- they are arranged in the form of concentric circles and are the site of conidia formation;
- the fruit turns black or brown;
- further infection of nearby apples occurs;
- as they ripen, the number of affected fruits also increases;
- if the fruit remains hanging on the tree, then the fungus along the stalk from it falls on the fruit branch, the fruit;
- this causes infection of nearby branches in which the fungus will winter;
- in spring, the infection continues to spread to the young ovary;
- wilting, with the subsequent death of overgrown branches.

Symptoms of a monilial burn:
- flowers turn brown or black;
- over time, they dry out;
- then the disease spreads to the ovaries, twigs and fruit twigs;
- on them, the leaves begin to turn brown and shrink;
- the affected leaves do not fall off and gradually take on a charred black appearance.

How to fight?
This disease is very harmful to the tree, therefore rot requires consistent treatment.
The main methods of combating moniliosis and its prevention include:
- pruning branches that have dried ends, black leaves and mummified apples;
- burning cut branches and mummified fruits;
- timely harvesting of apples;
- protection of fruits from various mechanical damage during their removal and transportation;
- storage of apples at a temperature of about 0 ° C;
- mandatory disinfection of storage and containers;
- treatment of the apple tree during the growing season with various preparations (for example, fungicides);
- spraying should be carried out periodically;
- to carry out timely treatment of other diseases;
- to carry out the treatment of infectious infections;
- protection of trees from mechanical damage;
- insect control (especially with the goose, moth, sawfly).
The above procedures should be carried out throughout the entire fertile period, as well as before and after it.
Video "Prevention of fruit rot of apple trees"
In addition to measures to combat fruit rot, see the video below.
Knowing the main reasons for the development of fruit rot, the first symptomatic manifestations, as well as measures to combat it, you can effectively resist this dangerous disease.
