Cherry diseases and their treatment with photos and videos
If you think that with the planting of cherry seedlings your mission is over, you are deeply mistaken. To achieve a good harvest, you need to provide the trees with proper care. And also monitor their health. To your attention the most dangerous cherry diseases, methods of their treatment. Photos will help us figure it out.
Common Factors Causing Cherry Disease:
- climate;
- weather;
- correctness, peculiarity of care;
- soil condition;
- injury to a tree;
- implementation or absence of preventive measures;
- the presence of other fruit trees in the garden;
- destruction (or not) of pests;
- other unpredictable factors.
Content
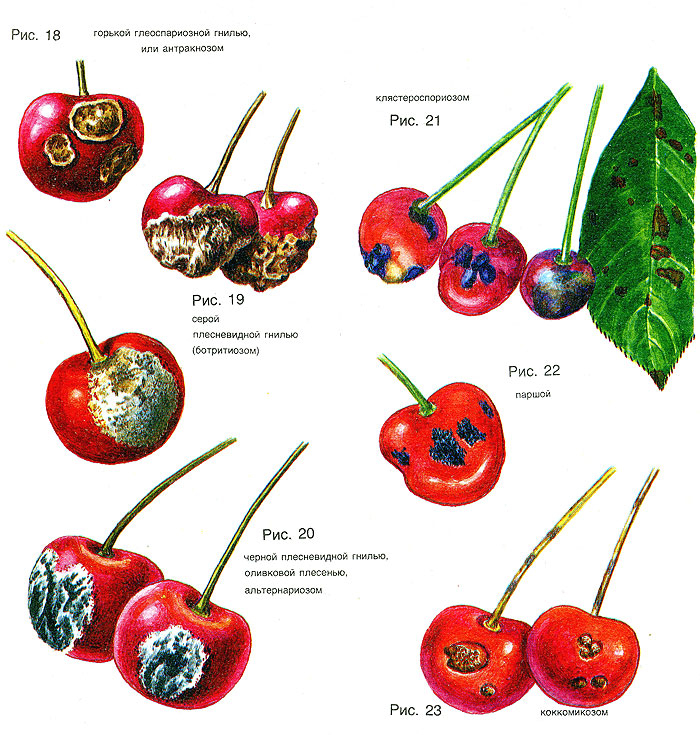
Hole spot
Clasterosproiosis is a common stone fruit disease caused by a fungus. High humidity in hot or warm weather contributes to its appearance. For wintering, spores of the fungus choose the affected places of the cherry. They contaminate healthy tissues. The pathogen is carried by rain, wind, insects.
The first symptoms of the disease are noticed already in early spring. The leaves are covered with dotted spots. Their red color gradually turns to brown. The spots have a crimson blurred border. This distinguishes hole spotting from other fungal diseases of cherry.
The diameter of the spots soon becomes 5 mm. In their place, due to drying, holes appear (hence the name of the disease). Soon the leaves are full of holes. In addition to leaves, flowers, cuttings, buds, and fruits are affected. Young infected shoots are distinguished by bright red edging, which increases in length. They secrete a liquid (gum). If the sprouts are severely affected, then soon they dry up, then fall off. Sick flowers darken, then crumble. The buds turn black, releasing gum, dry out, but remain on the tree. These signs are clearly conveyed by the picture.
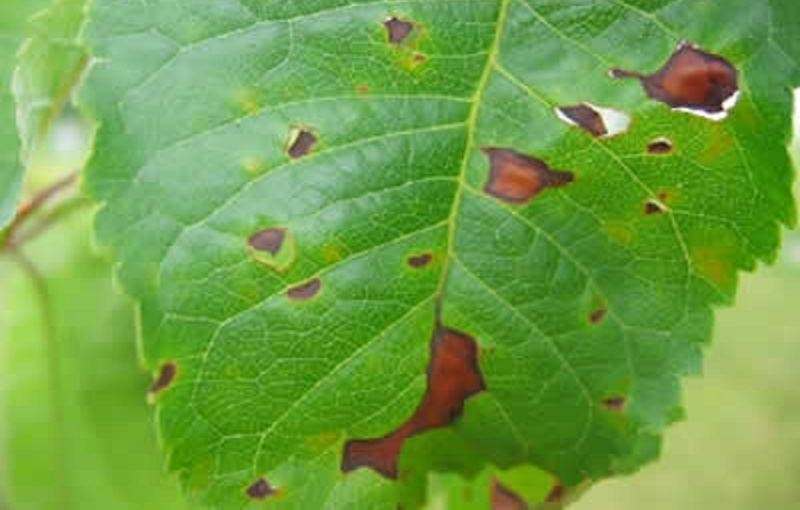

Control methods:
- Prune diseased branches. Disinfect the cut site with a thick solution: 1% copper sulfate plus 3% iron sulfate. Then grease with garden putty;
- Burn the fallen leaves, flowers, cut shoots immediately. Dig up this place;
- Spray the tree twice with 3% Bordeaux liquid for large lesions.
Coccomycosis
The disease came from Scandinavia (middle of the last century). Received mass distribution. The fungal pathogen is preserved by cherry leaves, living there in winter. Weakened plants are most susceptible to coccomycosis.
Most of the leaves suffer from this disease. They are covered with brown dots that grow to spots. The bottom plate of the leaf is covered with a pink-white bloom. This is where the spores of the parasite are located. Soon, all affected foliage crumbles. Less often cherry fruits are ill. They are covered with small dark dots and are deformed. You cannot eat such fruits!
Treatment for coccomycosis is the same as for perforated spot. Recently, breeders have developed varieties that are less prone to coccomycosis. They need less processing.
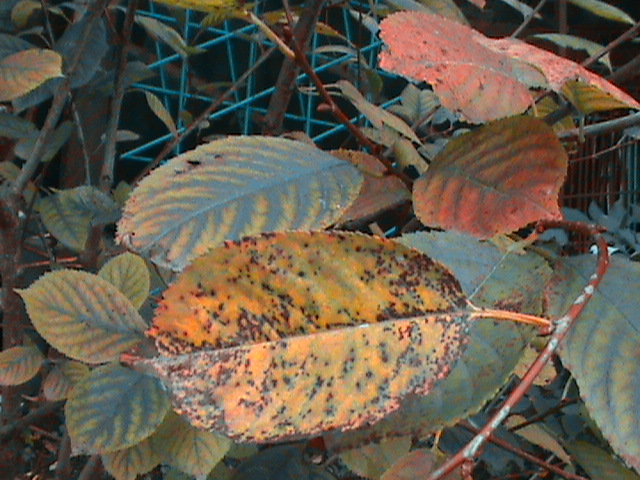

Moniliosis (gray rot)
This cherry disease is also known as monilial burn or gray rot. It is relatively "young" for our regions. It appeared only in the 90s of the last century.
The fungal pathogen lives in diseased parts of the tree. Here he will winter well, if preventive measures are not taken in a timely manner.
Almost all cherries are affected: foliage, trunk, shoots, fruits. Therefore, moniliosis is considered the most formidable disease. Sore areas look like burns.The leaves are infected first. Then the bark of the plant is covered with gray growths. They are located chaotically. Where such "burns" appear, the site begins to rot.
Affected shoots crack, releasing gum. Then they die. The berries are deformed, almost all of them crumble.
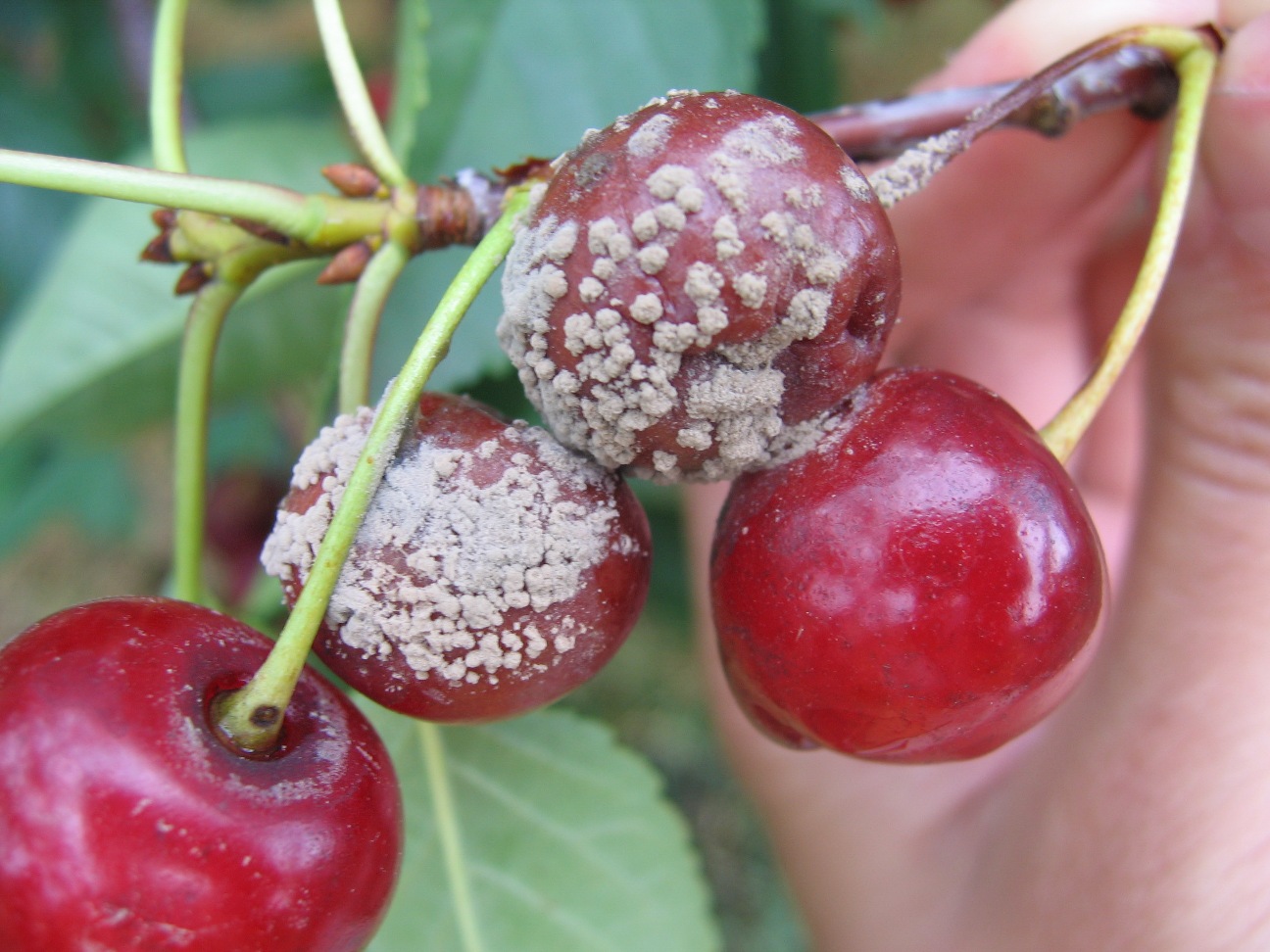

Control methods:
- The fallen diseased parts of the tree must be immediately burned;
- Cut off the branches - 10 centimeters below the affected area. Disinfect, treat with garden putty;
- Strip the bark of the trunk to healthy tissue;
- Spray the cherries with one of the preparations: 3% copper sulfate, Bordeaux liquid, nitrafen, iron sulfate, oleocobrite.
Anthracnose
Mostly cherry fruits are affected by the disease. The onset of the disease can be skipped. Since the fruits are immediately covered with barely noticeable light specks. Later, they become small tubercles with a pink bloom. In hot weather, cherries dry out. Wet weather can aggravate the course of the disease, destroying 80% of the fruit.
For the treatment of anthracnose, the chemical "Poliram" is used. They spray the plant three times: before flowering, after, and two weeks later again. This measure is sufficient for recovery.
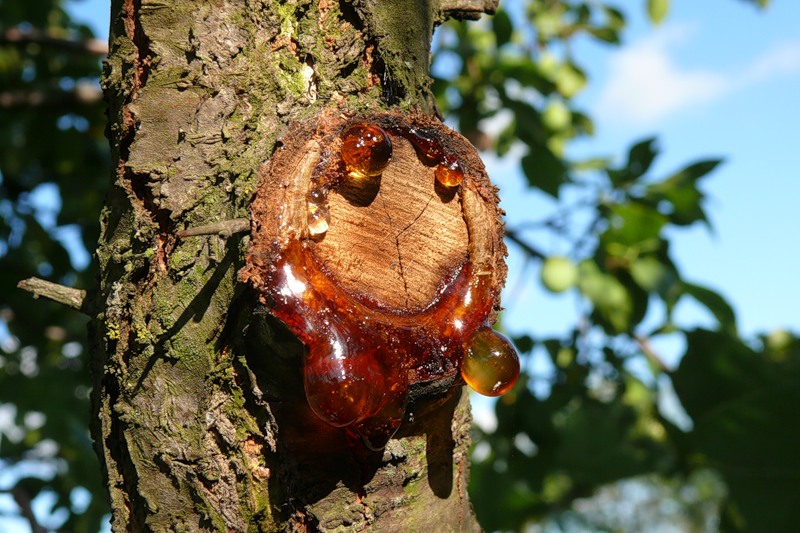
Gum therapy
All of the above cherry fungal diseases cause gum to leak from the affected parts. It is a clear liquid. As it flows out, the gum solidifies. This process is called gum flow. Possible reasons: abundant watering of the soil, excessive feeding.
It is imperative to fight gum disease. Since the liquid contains disease-causing spores, rain, wind, they will spread to healthy plants. Treatment consists in preventing, that is, preventing such a condition. First of all, you need proper care, destruction of pests, timely detection of diseases, and their treatment.
Rust
Cherry rust is caused by the parasitic fungus Thekopsora padi. The "hosts" of this pathogen are coniferous trees: spruce, juniper. Their cones contain spores that are carried to fruit trees by rain and wind.
Cherry leaves are covered with reddish spots. Their yellow border reminds rust... Hence the name. The upper side of the leaf shows signs more clearly than the lower one.

Treatment:
- Remove coniferous stands growing nearby;
- Collect and dispose of all diseased leaves;
- After flowering, spray the cherry with the chemical "Hom" (it contains copper oxychloride). Dilute a bucket of water with 80 grams of powder;
- When the cherries are harvested, sprinkle with 1% Bordeaux liquid.
Scab
Scab is a rather dangerous cherry disease caused by a pathogenic fungus or bacteria. Infection occurs during the flowering period. Damp weather contributes to the spread.
Spores of the pathogen appear on the foliage with brown-olive velvety spots. Cherry fruits may be affected. Mature ones - are covered with cracks, green ones - wrinkle, stop developing. In the presented photos, you can clearly see all the signs of cherry diseases.

Scab treatment measures are reduced to prevention.
- In early spring, sprinkle cherries and soil with nitrafen;
- When the buds begin to bloom, treat the trees with Bordeaux liquid (10 liters - 100 grams);
- After three weeks, when the flowering ends, repeat the previous procedure;
- Spray the third time after the fruit has been completely harvested;
- In case of severe infestation, you can make a fourth spraying two weeks after the third.
Cherry disease prevention and consequences
- First of all, proper care of fruit trees minimizes the risk of infection;
- Timely collect, burn fallen, diseased parts of the tree;
- Pruning of affected branches is best done in autumn in dry weather, before the foliage falls. Rain can spread disease-causing spores;
- Mid-spring - cut off all weak, dried shoots, branches that thicken the crown.This will give the tree the extra nutrients it needs to grow;
- Make sure that the near-stem circle is cleaned during fertilization;
- Protect cherries from injury. If there are any, then delete the branches that can no longer be saved. Clean the remaining wounds, lubricate with garden putty;
- Avoid sunburn of foliage, frostbite (whitewash the trunks with lime in time);
- Remove the gum in a timely manner. Treatment with vitriol will prevent gum flow;
- Spray the plant in the spring with 1% Bordeaux liquid, before the buds bloom. The second time to do the processing after flowering. The third is in two weeks. Autumn spraying is also effective when foliage falls. Held annually;
- Carefully treat trees with chemicals, otherwise there may be burns. Especially it rocks Bordeaux liquid. To prevent this, it is necessary to make a "control" spraying of one branch. The burn will appear as a necrotic spot. A fruit, a leaf - like a net. Then you need to temporarily stop processing.
These diseases harm not only cherries, but the entire garden plot. The yield of fruit trees decreases. Leaves fall prematurely. The appearance of the fruits deteriorates. Plant growth is inhibited. Their immunity decreases.
Remember:
- After the spread of infections, fruit trees need careful, proper care. Then a rich harvest can be expected;
- After processing, rinse the berries thoroughly under running water;
- Specialized stores will provide you with a large selection of ready-made preparations for plant processing;
- It should be remembered about the high toxicity of copper sulfate. Use it carefully. If necessary, you can change to another drug. Less toxic, for example "Fundazol". It is especially effective in flowering;
- It is good when as many leaves as possible are preserved on the tree. Then it will endure the winter better;
Video "Diseases of cherries - coccomycosis"
What to do if the leaves have flown around the cherry, you will learn from the video:
